ACUPUNCTURE & WELLNESS BLOG
Explore the intersection of ancient medicine and modern health through practical insights and easy-to-follow tips
EXPLORE MORE BELOW
Acid Reflux: An Acupuncture + Eastern Medicine Perspective on a Modern Epidemic
Acid reflux. GERD. Heartburn. Whatever name it goes by, it’s become a staple in the lives of far too many. Whether triggered by stress, food, or an overtaxed system, the burning in the chest and sour taste in the mouth are often treated with quick fixes like antacids or proton pump inhibitors.
Acid reflux. GERD. Heartburn. Whatever name it goes by, it’s become a staple in the lives of far too many. Whether triggered by stress, food, or an overtaxed system, the burning in the chest and sour taste in the mouth are often treated with quick fixes like antacids or proton pump inhibitors.
But what if there’s a deeper story here? One that speaks not only to the symptom, but to the pattern beneath it? Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM) offers a refreshingly holistic, layered approach to this all-too-common condition—one that sees reflux not as a malfunction, but as a message.
What Is Acid Reflux (GERD)?
In Western medicine, GERD occurs when stomach acid flows backward into the esophagus due to a weakened lower esophageal sphincter (LES). Over time, this can cause esophageal irritation and a cascade of symptoms:
• Burning chest sensation (heartburn)
• Sour or bitter taste in the mouth
• Regurgitation of food or fluid
• Bloating, nausea, hiccups
• Chronic cough or throat clearing
Conventional treatment often includes acid-suppressing medications. But suppressing acid doesn’t always address the cause—it often just mutes the messenger.
How Acupuncture Helps—The Physiological Angle
Acupuncture offers measurable support for acid reflux by:
• Improving esophageal motility and sphincter tone
• Reducing inflammation in the GI tract
• Enhancing vagal nerve activity, which governs digestion
• Calming the nervous system, reducing stress-triggered flare-ups
• Regulating gastric emptying, minimizing stagnant food and gas buildup
This isn’t just theoretical—clinical studies have shown acupuncture to reduce reflux episodes and improve quality of life in GERD patients.
The CCM View: When Stomach Qi Reverses
In Classical Chinese Medicine, acid reflux is understood as Stomach Qi counterflow (胃气上逆). Stomach Qi should descend. When it rises instead, we feel nausea, belching, burning, even vomiting. But why is it rebelling?
Here’s where CCM gets interesting. The rebellion is never random. It reflects a deeper disharmony in the system’s orchestration—often involving the Liver, Spleen, Shaoyang Pivot, or even the Heart-Kidney axis.
Common CCM Patterns Behind Reflux
1. Liver Overacting on Stomach (Wood Insulting Earth)
Presentation: Reflux triggered by stress or emotions. Rib-side tension, sighing, irritability, and a wiry pulse.
CCM Insight: The Liver constrains the smooth movement of Stomach Qi, causing it to rebel upward.
Acupuncture Strategy: Soothe Liver, harmonize Earth.
Points: LV14, LV3, PC6, ST36, SP4
2. Shaoyang Disharmony (Pivot Blockage)
Presentation: Alternating symptoms—hot/cold, bitter taste, dry mouth, nausea, or vague digestive discomfort.
CCM Insight: The Shaoyang is the body’s pivot; when it’s blocked, up and down get confused.
Acupuncture Strategy: Harmonize the pivot and release the exterior.
Points: GB41–SJ5 pair, GB34, PC6
3. Stomach Heat or Damp-Heat
Presentation: Burning, acid taste, foul breath, yellow coating, irritability.
CCM Insight: Heat forces acid upward and disturbs digestion.
Acupuncture Strategy: Clear Stomach Heat, drain Damp.
Points: ST44, LI11, REN12, PC6, SP9
4. Spleen Qi Deficiency with Cold
Presentation: Watery reflux, bloating, fatigue, cold limbs, loose stools. Worsens with raw or cold foods.
CCM Insight: Weak digestion can’t transform food; turbid yin rises instead of clear yang descending.
Acupuncture Strategy: Warm the middle, support transformation.
Points: REN12, ST36, SP6, DU4, REN6
5. Shaoyin Imbalance (Heart-Kidney Axis)
Presentation: Reflux worse at night, with anxiety, insomnia, or palpitations. Symptoms may feel “heat rising.”
CCM Insight: When Heart Fire isn’t rooted in Kidney Water, fire floats upward—burning the throat and chest.
Acupuncture Strategy: Anchor Heart Fire, root it in Water.
Points: HT7, KI3, PC6, REN14, Yin Tang
✨ From Suppression to Harmonization
What sets the CCM approach apart is that we don’t suppress the acid—we listen to the body’s message. Reflux is not the enemy; it’s a sign of miscommunication between organ systems, often driven by deeper stress, dietary mismatch, or constitutional weakness.
Acupuncture becomes more than symptom relief—it becomes re-patterning. A way to realign the channels, restore digestive harmony, and create space for long-term healing.
Final Thoughts: When the Middle Burner Speaks
The Stomach and Spleen—our “Middle Burner”—are central in Chinese medicine for a reason. When they are harmonized, the entire system thrives. When they’re out of balance, symptoms like reflux, fatigue, and fog creep in.
But there is a way back. One that doesn’t ignore the symptom, but rather uses it as a doorway into a deeper dialogue. Acupuncture—when guided by the wisdom of the classics—offers that pathway.
If you’re living with reflux, you don’t have to live in suppression mode. You can live in rhythm again.
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Through the Lens of Acupuncture + Classical Chinese Medicine
In a world where autoimmune diseases are on the rise, Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis has become a familiar yet often misunderstood diagnosis. While modern medicine recognizes it as the most common cause of hypothyroidism in iodine-sufficient regions, there’s a richer, more nuanced way to understand this condition—one that speaks to root causes, constitution, and the dynamic intelligence of the body.
In a world where autoimmune diseases are on the rise, Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis has become a familiar yet often misunderstood diagnosis. While modern medicine recognizes it as the most common cause of hypothyroidism in iodine-sufficient regions, there’s a richer, more nuanced way to understand this condition—one that speaks to root causes, constitution, and the dynamic intelligence of the body.
Let’s explore Hashimoto’s through both biomedical and Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM) perspectives, and look at how acupuncture can be a profound support on this journey.
🌿 What Is Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis?
Hashimoto’s is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to chronic inflammation and gradual loss of thyroid function. Symptoms may include:
• Fatigue and brain fog
• Cold intolerance
• Weight gain
• Dry skin and hair thinning
• Constipation
• Irregular or heavy menstruation
• Depression or anxiety
• Goiter (thyroid enlargement)
Bloodwork often reveals elevated thyroid antibodies (anti-TPO, anti-thyroglobulin) and signs of low thyroid function (elevated TSH, low free T4).
✨ How Acupuncture Helps—Physiologically Speaking
From a biomedical angle, acupuncture offers tangible benefits:
• Regulates the immune system: It can modulate immune response and reduce inflammatory cytokines, calming the autoimmune attack.
• Balances the nervous system: Acupuncture soothes the HPA axis (stress response) and supports the HPT axis (thyroid regulation).
• Improves circulation and energy flow: It enhances blood flow to the thyroid, improves lymphatic drainage, and supports detoxification.
• Supports mood and metabolism: By regulating neurotransmitters and hormones, acupuncture helps address the anxiety, depression, and metabolic sluggishness common in Hashimoto’s.
🌀 The Classical Chinese Medicine View
In CCM, we don’t treat “Hashimoto’s” as a single disease. We ask deeper questions:
• What constitutional terrain allowed this to develop?
• What layer of the system is disturbed?
• Is this a loss of yang fire, an accumulation of cold, or a disconnection between fire and water?
Most often, Hashimoto’s points to a Shaoyin pattern: a breakdown between the Heart (Fire) and Kidney (Water) axis.
In Chapter Nine of Classical Chinese Medicine by Liu Lihong, this Shaoyin dynamic is explored in depth:
“The fire of the sovereign has lost its envoy. Without Water to anchor it, Fire flares upward or collapses inward, leaving the system cold, weak, and disoriented.”
This poetic image maps onto a real-world experience: cold hands and feet, fatigue, depression, dryness, night sweats, anxiety, and a deep inner sense of burnout or withdrawal from the world.
🔬 Common CCM Patterns in Hashimoto’s
1. Shaoyin Deficiency (Kidney-Heart Axis)
• Fatigue, fearfulness, poor sleep, low libido, cold intolerance
• Treatment: Restore the communication between Fire and Water (e.g., DU4, KI3, HT7, REN4)
2. Taiyin Dampness (Spleen involvement)
• Brain fog, bloating, loose stools, phlegm nodules, weight gain
• Treatment: Transform dampness, support Spleen Qi (e.g., ST36, SP9, REN12)
3. Jueyin Wind (Liver involvement)
• Fluctuating symptoms, mood swings, frustration
• Treatment: Harmonize the Wood element, anchor yang (e.g., LV3, PC6, GB34)
🌿 Acupuncture Treatment Strategies
Each case is unique, but common approaches include:
• Tonify Kidney Yang and Mingmen Fire: DU4, REN4/6, KI3, moxibustion
• Regulate the Shaoyin Axis: HT7, KI6, PC6
• Resolve Phlegm and Nodules: ST40, REN22, LI4, SP6
• Calm the Shen: Yintang, Anmian, HT7
• Support the Spleen: ST36, SP9, REN12 (especially in damp presentations)
This isn’t a one-size-fits-all protocol—it’s tailored, responsive medicine, rooted in observation, pulse and tongue diagnosis, and the story of the person, not just the labs.
🪷 Final Thoughts: From Diagnosis to Dialogue
Hashimoto’s is not the end of a conversation—it’s the beginning of a deeper one.
In the CCM view, the body is always speaking, always reaching toward balance. What we call “autoimmunity” may be an overwhelmed system crying out for restoration, rhythm, and reconnection. Acupuncture offers a powerful way to listen to that cry—not to silence it, but to respond.
If you or someone you know is navigating life with Hashimoto’s, know that there is a map—one that sees the body not as broken, but as beautifully complex and worthy of being understood.
What Is the ‘Pivot’ in Your Body—and What Happens When It Gets Stuck?
Understanding the Shaoyang Layer and Its Role in Hormonal Balance and Stress
In Classical Chinese Medicine, the body is not a machine composed of parts but a dynamic field of resonance—perpetually adjusting, mediating, and transforming. Nowhere is this more evident than in the realm of the Shaoyang, the “pivot” of the body.
But what exactly is this “pivot,” and why does it matter?
Understanding the Shaoyang Layer and Its Role in Hormonal Balance and Stress
In Classical Chinese Medicine, the body is not a machine composed of parts but a dynamic field of resonance—perpetually adjusting, mediating, and transforming. Nowhere is this more evident than in the realm of the Shaoyang, the “pivot” of the body.
But what exactly is this “pivot,” and why does it matter?
The Shaoyang: Where Inner Meets Outer
According to the Shanghan lun and Jingui yaolue, the Shaoyang is one of the six conformations, a unique phase between the exterior (Taiyang) and interior (Yangming). It is neither fully inside nor fully outside, neither wholly yin nor wholly yang. As Liu Lihong notes in Classical Chinese Medicine, it is the mechanism of pivoting (樞 shū)—the place of movement, regulation, and transformation.
The Shaoyang corresponds to the Gallbladder and Sanjiao—organs not easily defined by modern anatomy but crucial in managing transitions: day to night, stress to rest, ovulation to menstruation, youth to maturity. It’s the body’s hinge point, the axis of negotiation.
When the Pivot Gets “Stuck”
When the Shaoyang becomes stagnant, we see conditions that are stuck in limbo—neither resolving nor clearly manifesting. This might look like:
• Cyclical or alternating symptoms (e.g., chills and fever, mood swings, bloating that comes and goes)
• Hormonal imbalances: PMS, irregular periods, perimenopausal shifts
• Stress-related stagnation: irritability, rib-side discomfort, insomnia
• Digestive irregularity that mirrors emotional fluctuations
• Mental-emotional states that vacillate—feeling “neither here nor there”
The classic presentation of Shaoyang disorder includes symptoms such as a bitter taste in the mouth, dry throat, dizziness, and a wiry pulse. These signs speak of a system caught between pushing forward and holding back.
The Stress-Hormone-Pivot Connection
Modern stress physiology mirrors this classical wisdom. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis is our stress-response system. It’s deeply involved in how we transition through daily rhythms and life stages—just like the Shaoyang.
Chronic stress keeps the pivot open or stuck mid-motion, never completing a cycle. In women, this can affect the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis, leading to the typical cascade of perimenopausal symptoms: hot flashes, mood changes, insomnia, fatigue, and irregular cycles.
Shaoyang harmonization, therefore, becomes essential—not only for acute external invasions but for these internal, chronic, and life-phase-related imbalances.
Pivoting Toward Balance
The harmonizing strategy seen in Xiao Chai Hu Tang (Minor Bupleurum Decoction) is not about suppressing or purging. It’s about giving the body space to pivot. This gentle coaxing—neither pushing nor retreating—is profoundly effective for modern conditions rooted in stuck transitions.
In clinical practice, we might not always reach for formulas like Xiao Chai Hu Tang directly. But we think in terms of pivot: Is this patient stuck between stress and surrender, between menstruation and menopause, between emotional suppression and expression?
When we treat the pivot, we restore motion. When we restore motion, transformation can occur.
Honey, under a microscope
Magnified by 25x.
That is the post! Nature provides such nourishment and beauty. ❤️ 🐝
Magnified by 25x.
That’s it, that is the post! Nature provides such nourishment and beauty. ❤️ 🐝
ACUPUNCTURE | ROCHESTER, NY
Navigating 2025: The Year of the Wood Snake
As we step into 2025, we welcome the Year of the Wood Snake, a time infused with wisdom, transformation, and strategic growth. The interplay of Wood and Fire elements this year brings both opportunities and challenges, requiring adaptability, patience, and deep introspection. Whether you follow Chinese metaphysics for personal development, business success, or health insights, understanding the energy of the Wood Snake can help you navigate the year with clarity.
As we step into 2025, we welcome the Year of the Wood Snake, a time infused with wisdom, transformation, and strategic growth. The interplay of Wood and Fire elements this year brings both opportunities and challenges, requiring adaptability, patience, and deep introspection. Whether you follow Chinese metaphysics for personal development, business success, or health insights, understanding the energy of the Wood Snake can help you navigate the year with clarity.
Understanding the Wood Snake Energy
The Chinese zodiac consists of twelve animal signs, each cycling through the five elements—Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water. This year, we see the combination of the Snake (Si) with Yin Wood (Yi), forming a unique energetic landscape.
Snake Characteristics: The Snake is associated with intelligence, transformation, mysticism, and strategic thinking. It is perceptive, calculating, and introspective.
Wood Element: Wood represents growth, expansion, and innovation. It seeks progress but can become restless or overextended.
Fire Element: The Snake is naturally linked to Fire, which brings passion, action, and sometimes volatility.
The Wood-Fire Dynamic: Wood feeds Fire, fueling creativity, leadership, and breakthroughs but also posing risks of overextension or burnout.
This year carries a deep call for introspection and careful planning. It’s a year where patience, adaptability, and strategic moves will yield the best results.
Themes of 2025: Lessons, Karma, and Opportunities
1. Transformation and Revolution
One of the key hexagrams for 2025 is Hexagram 49: Revolution (Reform). This suggests significant shifts on personal, societal, and global levels. Change is inevitable, and those who embrace transformation will find themselves ahead of the curve.
2. Yin and Yang Balance
The Year of the Wood Snake emphasizes balance between stillness and movement, planning and execution. The Snake’s wisdom advises us to think before we act and to make decisions based on strategy rather than impulse.
3. Destiny, Luck, and Choices
Luck is not random. It is shaped by our actions, mindset, and ability to align with natural rhythms. This year, being mindful of your goals and ensuring they are congruent with your actions will be crucial for success.
4. The Influence of the Five Elements
Each element plays a role in shaping the energy of the year:
Wood (Anger, Growth, Ambition)
Fire (Joy, Passion, Success)
Earth (Stability, Nourishment, Worry)
Metal (Discipline, Authority, Grief)
Water (Wisdom, Fear, Adaptability)
The dominance of Wood and Fire suggests an active, forward-moving year but also highlights potential areas of stress if balance is not maintained.
Personal and Professional Insights for 2025
1. Business and Career
The energy of the Wood Snake supports:
Strategic planning and long-term investments.
Networking and forming beneficial alliances.
Creativity and innovation, particularly in technology and AI.
Financial caution—high-risk investments may be volatile.
2. Health and Well-being
The dominant elements in 2025 indicate:
A need for balance between movement and rest.
Potential stress-related issues due to overwork and overcommitment.
Heart, circulation, and nervous system may be areas of concern (Fire element).
Digestive health and immunity require care (Wood and Earth interaction).
3. Relationships and Emotional Growth
The Wood Snake year encourages deep, meaningful connections:
Romantic passion and flirtation will be heightened, making it a good year for deepening commitments.
Emotional wisdom and transformation will be key—relationships that are built on trust and mutual growth will thrive.
Compatibility for the Year: The Monkey, Rooster, and Ox will have particularly good relationship luck this year.
Global and Environmental Influences
The year is marked by wind and heat, suggesting climatic shifts, possible earthquakes, and an increase in fires.
Political and social movements may be prominent, as Fire energy can drive revolutionary change.
Technological advancements, particularly in AI and digital finance, will see significant leaps.
How to Align with the Wood Snake Energy
Cultivate Wisdom and Patience – Think before acting, embrace learning, and avoid impulsive decisions.
Focus on Strategic Growth – Plan long-term, set clear goals, and move forward step by step.
Mind Your Health – Avoid overexertion, balance work and rest, and nourish your body with grounding foods.
Embrace Change – This is a year of transformation; resisting change may lead to unnecessary struggles.
Deepen Relationships – Strengthen your connections through trust, communication, and shared goals.
Walking the Serpent’s Path: A Year of Transformation
The Year of the Wood Snake is a time of wisdom, strategy, and transformation. By aligning with its energies—balancing action with reflection, ambition with patience, and passion with discernment—you can make the most of what 2025 has to offer.
ACUPUNCTURE | ROCHESTER, NY
Stuck Energy: Understanding Liver Qi Constraint in Chinese Medicine
Have you ever felt like you’re on edge for no clear reason? Maybe you’re irritable, sighing a lot, or feeling like there’s a lump in your throat when you’re upset? If so, your body might be dealing with something called Liver Qi Constraint.
Have you ever felt like you’re on edge for no clear reason? Maybe you’re irritable, sighing a lot, or feeling like there’s a lump in your throat when you’re upset? If so, your body might be dealing with something called Liver Qi Constraint.
What Is Liver Qi?
In Chinese medicine, the Liver isn’t just a physical organ—it’s responsible for the smooth flow of Qi (energy) throughout the body. When your Qi moves freely, you feel relaxed and balanced. But when it gets stuck, it’s like a traffic jam in your system—everything slows down, pressure builds, and emotions can run high.
What Causes Liver Qi to Get Stuck?
Liver Qi Constraint is often caused by stress, frustration, or emotional repression. Modern life is full of deadlines, social pressures, and responsibilities, and when we don’t have a healthy way to release these tensions, they can get trapped in the body.
Other common triggers include:
✔️ Overthinking or worrying too much
✔️ Holding in emotions instead of expressing them
✔️ A sedentary lifestyle with little movement
✔️ Poor diet—especially too much greasy, spicy, or processed food
Signs That Your Liver Qi Might Be Stagnant
If Liver Qi isn’t flowing smoothly, it can lead to a variety of symptoms, including:
🔹 Feeling easily irritated or short-tempered
🔹 Frequent sighing (your body’s attempt to move stuck energy)
🔹 A tight sensation in the chest or throat (Plum Pit Qi)
🔹 Digestive discomfort, bloating, or gas
🔹 Irregular or painful menstruation in women
🔹 Tension headaches, jaw clenching, or tight shoulders
How to Get Your Liver Qi Moving
The good news is that Liver Qi loves movement, expression, and flow! Here are some simple ways to help:
🌿 Move Your Body – Exercise, stretching, or even a short walk can help release stuck energy.
💨 Breathe Deeply – Focused breathing exercises (like belly breathing) can help Qi circulate.
💆♂️ Acupressure & Massage – Gently massaging the area between your ribs or pressing on the acupuncture point Liver 3 (on the top of your foot between the first and second toes) can help move stagnant Qi.
🍵 Drink Soothing Teas – Peppermint, chrysanthemum, or rose tea can help smooth the Liver’s energy.
😊 Express Yourself – Journaling, talking to a friend, or even yelling into a pillow (yes, really!) can help release pent-up emotions.
🥦 Eat Light & Green – Bitter greens like dandelion, kale, or arugula can help support the Liver’s function.
Acupuncture: A Powerful Tool for Freeing Stuck Qi
One of the most effective ways to release Liver Qi Constraint is through acupuncture. By inserting fine needles into specific points along the body’s meridians, acupuncture helps to:
✔️ Unblock stagnation – It encourages Qi to flow freely, relieving tension and stress.
✔️ Calm the nervous system – Acupuncture reduces stress hormones, helping you feel more relaxed and emotionally balanced.
✔️ Alleviate physical symptoms – Whether it’s digestive issues, headaches, or muscle tightness, acupuncture works to bring the body back into harmony.
Common acupuncture points used to soothe Liver Qi include:
🔹 Liver 3 (Tai Chong) – Located on the top of the foot, this point is excellent for getting Qi unstuck.
🔹 Gallbladder 34 (Yang Ling Quan) – Found on the outer lower leg, this point is great for tension and irritability.
🔹 Pericardium 6 (Nei Guan) – A go-to point for calming the mind and easing emotional stress.
Many people feel a sense of relief—even after just one session! But for deeper, long-term balance, regular treatments may be recommended.
When to Seek Help
If you’ve been feeling stuck for a while and lifestyle changes aren’t enough, working with an experienced acupuncturist or herbalist can be a game-changer. Chinese medicine has been treating Liver Qi Constraint for thousands of years with acupuncture, herbal formulas, and lifestyle recommendations.
Remember—your body is always communicating with you. If you feel stuck, frustrated, or overwhelmed, it might just be your Liver asking for a little help to get things flowing again.
ACUPUNCTURE | ROCHESTER, NY
Your Brain on Movement: How Sprinting Boosts Mental Clarity, Mood, and Neurotransmitter Balance
When we think about exercise, we often focus on the physical benefits—cardiovascular health, strength, endurance. But what about the brain? A fascinating study reveals that vigorous physical activity, like sprinting, triggers a biochemical shift in the brain, increasing levels of glutamate and GABA, two neurotransmitters crucial for mental clarity, emotional balance, and cognitive function.
When we think about exercise, we often focus on the physical benefits—cardiovascular health, strength, endurance. But what about the brain? A fascinating study reveals that vigorous physical activity, like sprinting, triggers a biochemical shift in the brain, increasing levels of glutamate and GABA, two neurotransmitters crucial for mental clarity, emotional balance, and cognitive function.
The Science of Exercise and Brain Chemistry
The study, conducted at UC Davis, used magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) to examine how high-intensity exercise (above 80% of max heart rate) affects neurotransmitter levels. The researchers found that after a bout of vigorous exercise:
✔ Glutamate levels increased – This neurotransmitter is essential for learning, memory, and overall brain function.
✔ GABA levels increased – Often referred to as the brain’s “brake pedal,” GABA promotes relaxation, emotional regulation, and stress reduction.
✔ The effects were strongest in the visual cortex and the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) – areas linked to focus, decision-making, and emotional processing.
Why This Matters for Mental Health and Cognitive Performance
Glutamate and GABA are major players in the balance between excitation and inhibition in the brain. An imbalance in these neurotransmitters has been linked to anxiety, depression, cognitive fog, and even neurodegenerative diseases. The fact that exercise naturally increases both suggests that movement could be a powerful, accessible intervention for mental well-being.
👉 Exercise as an Antidepressant: Research has already established that physical activity reduces symptoms of depression. This study helps explain why—by increasing neurotransmitter reserves, exercise may replenish what’s depleted in conditions like depression and anxiety.
👉 Brain Resilience and Plasticity: Since glutamate is involved in neuroplasticity, the ability to reorganize neural pathways, regular movement may contribute to better adaptability, learning, and even creative problem-solving.
Sprint Your Way to a Sharper Mind
You don’t need to be an elite athlete to reap these benefits. Short bursts of high-intensity activity—whether sprinting, fast cycling, jump rope, or even explosive bodyweight exercises—can trigger this biochemical shift.
Try this brain-boosting sprint protocol:
🏃 Warm-up – 5 minutes of dynamic stretching and light jogging.
🚀 Sprint – 20-30 seconds of all-out effort (running, biking, or any full-body explosive movement).
🚶 Recovery – 90 seconds of walking or slow movement.
🔁 Repeat – 4-6 rounds.
If sprinting isn’t your thing, other intense movement forms like kettlebell swings, hill climbing, or even fast-paced bodyweight circuits can create similar effects.
The Acupuncture Connection
Traditional Eastern medicine has long understood that movement influences mental and emotional health. While this study focuses on exercise, acupuncture has also been shown to regulate neurotransmitter balance, particularly GABA.
🔹 Acupuncture & GABA – Studies suggest acupuncture modulates GABA levels, which may explain its calming effects on the nervous system.
🔹 Breathwork & Glutamate – Slow, controlled breathing enhances oxygen and CO2 balance, indirectly supporting neurotransmitter metabolism.
This overlap suggests that combining exercise with acupuncture could create a synergistic effect, optimizing neurotransmitter function for both relaxation and cognitive clarity.
Final Thoughts: Move, Recover, Repeat
Sprinting, or any form of vigorous movement, doesn’t just strengthen the body—it resets the brain. Whether you’re looking for a natural antidepressant, a productivity hack, or a way to improve long-term brain health, movement is an essential (and free) tool.
Your challenge: Try a sprint-based workout this week and pay attention to how your focus, mood, and creativity shift in the hours afterward. Let movement be your medicine!
ACUPUNCTURE | ROCHESTER, NY
Understanding the Lymphatic System
Imagine a highway system in your body that carries waste, maintains fluid balance, and supports your immune defenses. That’s your lymphatic system, a crucial but often overlooked component of your health. Understanding how it works and its importance can help us better appreciate its role in keeping us healthy.
Imagine a highway system in your body that carries waste, maintains fluid balance, and supports your immune defenses. That’s your lymphatic system, a crucial but often overlooked component of your health. Understanding how it works and its importance can help us better appreciate its role in keeping us healthy.
What is the Lymphatic System?
The lymphatic system is a network of:
• Lymphatic vessels: These are similar to blood vessels but carry lymph, a clear fluid containing white blood cells, proteins, and waste products.
• Lymph nodes: Small, bean-shaped structures that filter lymph and house immune cells to fight infection.
• Other organs: The spleen, thymus, tonsils, and bone marrow are all part of the lymphatic system.
What Does the Lymphatic System Do?
The lymphatic system has three primary roles:
1. Fluid Balance
The lymphatic system ensures that excess fluid from tissues (called interstitial fluid) is collected and returned to the bloodstream, preventing swelling, or edema.
2. Immune Defense
Lymph nodes act as checkpoints, filtering out harmful pathogens like bacteria, viruses, and even cancer cells. White blood cells (lymphocytes) inside the nodes are your body’s first responders, initiating immune responses.
3. Waste Removal
It helps remove cellular waste, toxins, and other unwanted materials from tissues, supporting overall detoxification.
How Does It Work?
1. Lymph Formation: Fluid from tissues enters small lymph capillaries and becomes lymph.
2. Transportation: Lymph travels through larger lymphatic vessels, passing through lymph nodes for filtration.
3. Drainage into Bloodstream: Cleaned lymph eventually rejoins the circulatory system via the thoracic duct or right lymphatic duct.
Unlike the circulatory system, the lymphatic system doesn’t have a pump like the heart. Instead, it relies on muscle movement, breathing, and gravity to keep lymph moving.
Why is the Lymphatic System Important for Your Health?
• Fighting Illness: Lymph nodes swell when they detect infections, signaling your body is fighting off invaders.
• Reducing Inflammation: By draining fluid and toxins, the lymphatic system can help manage inflammation, which is often linked to chronic conditions.
• Supporting Detoxification: A healthy lymphatic system aids in eliminating waste products, enhancing energy levels and vitality.
Signs of a Sluggish Lymphatic System
When the lymphatic system isn’t functioning optimally, you may experience:
• Swelling in the arms or legs (lymphedema)
• Frequent infections
• Fatigue
• Skin issues like acne or rashes
How to Support a Healthy Lymphatic System
Here are some ways to boost your lymphatic health:
1. Stay Active: Regular exercise promotes lymph flow by contracting muscles.
2. Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain lymph fluid levels.
3. Lymphatic Massage: Gentle, targeted massages can stimulate lymph flow.
4. Deep Breathing: Diaphragmatic breathing acts as a natural pump for lymphatic fluid.
5. Healthy Diet: Eating a diet rich in antioxidants, fiber, and healthy fats supports lymphatic function.
The Connection Between the Lymphatic System and Acupuncture
From an Eastern medicine perspective, the lymphatic system aligns closely with the concept of fluid regulation and Qi movement. Acupuncture can enhance lymphatic flow by promoting circulation and addressing stagnation, making it a valuable therapy for conditions like swelling, inflammation, and low immunity.
Healthy Lymphatic Flow, Healthy Life
The lymphatic system is your body’s unsung hero, quietly working to keep you healthy by maintaining fluid balance, supporting immunity, and detoxifying your body. Simple lifestyle changes can make a big difference in keeping it functioning optimally. Whether through exercise, hydration, or therapies like acupuncture, supporting your lymphatic system is a key part of overall wellness.
Acupuncture Point Spotlight: San Yin Jiao
In Chinese Medicine, each acupuncture point has its own story and unique set of functions. One of the most versatile points is Sanyinjiao (SP-6), often referred to as the “Three Yin Intersection.” This blog post explores the origin of its name, its location, and the reasons why practitioners rely on SP-6 for a wide range of health concerns.
In Chinese Medicine, each acupuncture point has its own story and unique set of functions. One of the most versatile points is Sanyinjiao (SP-6), often referred to as the “Three Yin Intersection.” This blog post explores the origin of its name, its location, and the reasons why practitioners rely on SP-6 for a wide range of health concerns.
The Name: “Three Yin Intersection”
The Chinese name for SP-6, Sanyinjiao (三阴交), breaks down as follows:
• San (三): “Three”
• Yin (阴): Refers to the yin energy of the body, specifically the yin meridians
• Jiao (交): “Intersection” or “Crossing”
This point is called the “Three Yin Intersection” because it is the convergence point of three primary yin channels—the Spleen, Liver, and Kidney meridians. This strategic meeting place explains its powerful ability to influence multiple aspects of the body simultaneously, making it a mainstay in countless TCM treatment protocols.
Location and How to Find It
SP-6 lies on the medial (inner) side of the lower leg, approximately 3 cun (body-inches) above the medial malleolus (the prominent bone on the inner ankle), just behind the medial border of the tibia. A quick way to locate it is by placing four finger-widths (your own fingers) above the tip of the medial malleolus, on the soft tissue just behind the tibia.
Energetic Functions
1. Strengthens Spleen Qi: SP-6 helps the Spleen regulate digestion, addressing issues like bloating, loose stools, and low energy.
2. Nourishes Blood and Yin: By intersecting with the Kidney and Liver channels, SP-6 effectively supports blood and yin. This makes it invaluable for those experiencing symptoms of yin deficiency, such as insomnia or dry skin.
3. Harmonizes the Liver: SP-6 is renowned for helping to soothe Liver Qi stagnation, offering relief from stress, irritability, and premenstrual tension.
4. Supports Kidney Function: With its connection to the Kidney channel, SP-6 promotes reproductive health and balance in the genitourinary system. It can be a key point in protocols for fertility and hormonal regulation.
5. Regulates Menstruation and Gynecological Conditions: The “go-to” point for a range of menstrual and gynecological issues, including cramps (dysmenorrhea), irregular cycles, pelvic pain, and postpartum recovery.
6. Calms the Mind: Often added to treatments aimed at soothing anxiety, relieving restlessness, or improving sleep quality.
Common Indications
• Digestive complaints: Bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, or reduced appetite
• Menstrual disorders: Dysmenorrhea, irregular cycles, PMS
• Pelvic issues: Uterine prolapse, lower abdominal discomfort
• Sleep disturbances: Insomnia, restless sleep
• Stress and anxiety: Emotional turbulence, irritability
• Lower leg discomfort: Cramps, swelling, or tension in the medial side of the calf
Needling and Sensations
Acupuncturists typically needle SP-6 to a depth of about 0.5 to 1.5 cun, depending on a patient’s body type and the specific treatment strategy. Patients often feel a dull or heavy sensation that may radiate up or down the leg, indicative of qi activation in the channel.
Special Considerations
Pregnancy: SP-6 is avoided or used with great caution during pregnancy due to its potential to stimulate uterine contractions. Because it intersects three yin channels, SP-6 can be quite powerful. Practitioners will tailor the needle technique and duration to an individual’s constitution and specific health goals.
In a Nutshell
Sanyinjiao (SP-6) is a cornerstone in acupuncture and TCM treatments. As the intersection point of three critical yin channels—Spleen, Liver, and Kidney—it exerts far-reaching influence on digestion, reproductive health, and mental-emotional well-being. Whether you’re new to acupuncture or a long-time patient, understanding the role of SP-6 can shed light on why your practitioner may include it in your treatments. Interested in experiencing the therapeutic effects of Sanyinjiao? Talk to your acupuncturist about how SP-6 might fit into your overall wellness plan. This powerful point, when used appropriately, can help address concerns ranging from stress relief to menstrual support, making it a trusted ally in many TCM treatment strategies.
ACUPUNCTURE | ROCHESTER, NY
Embracing Discomfort: The Surprising Path to Wellness
In our modern world, filled with comforts and conveniences our ancestors could never have imagined, many of us find ourselves paradoxically more stressed, anxious, and unfulfilled. From central heating to smartphones, these advances have created an environment where discomfort is minimized—yet, this constant pursuit of ease may be causing more harm than good.
In our modern world, filled with comforts and conveniences our ancestors could never have imagined, many of us find ourselves paradoxically more stressed, anxious, and unfulfilled. From central heating to smartphones, these advances have created an environment where discomfort is minimized—yet, this constant pursuit of ease may be causing more harm than good.
The Ancient Connection Between Pleasure and Pain
Greek philosopher Dio Chrysostom observed over two millennia ago that a life of luxury dulls our ability to endure pain and diminishes the joys we can feel. Modern neuroscience echoes this sentiment, showing that pleasure and pain are processed in overlapping brain regions. This balance, when tipped excessively toward pleasure, triggers compensatory mechanisms that make us more sensitive to pain over time.
Anne Lembke, author of Dopamine Nation, describes this dynamic as a “pleasure-pain balance.” Overindulgence in pleasures like sugary foods, social media, or alcohol can lead to a cycle of tolerance, overconsumption, and ultimately a state where even small discomforts feel unbearable.
The Problem of “Comfort Creep”
Michael Easter, in his book The Comfort Crisis, explains that as new comforts emerge, our expectations adjust, rendering previous comforts insufficient. This “comfort creep” shrinks our tolerance for discomfort and discourages the physical activity and mental resilience necessary for health. For example, the sedentary lifestyles many of us lead—enabled by cars, delivery services, and desk jobs—stand in stark contrast to the physically demanding lives of our hunter-gatherer ancestors, who often walked or ran 25 miles daily to secure food.
How Discomfort Can Heal Us
The good news is that discomfort, when approached intentionally, can restore balance and lead to lasting well-being. Studies show that activities involving temporary pain, such as exercise or cold water immersion, can trigger the body’s homeostatic mechanisms, tipping the pleasure-pain balance toward enduring pleasure.
Lembke highlights the benefits of abstaining from overindulgence. A period of just four weeks without a “drug of choice”—whether that’s excessive screen time or unhealthy snacks—can reset our brain’s reward pathways, allowing us to take joy in simpler, healthier pleasures.
Practical Ways to Reintroduce Discomfort
1. Move More: Incorporate physical activity into your daily routine. Even short bursts of exercise can boost mood and reduce cravings for unhealthy indulgences.
2. Fast Occasionally: Practices like intermittent fasting echo the eating patterns of our ancestors and can improve metabolic health.
3. Limit Digital Overload: Use timers or app restrictions to curb excessive screen time and reclaim mental clarity.
4. Embrace Environmental Challenges: Try cold water exposure, or simply spend more time outside in varying weather conditions to build resilience.
5. Set Lofty Goals: Pursue challenges that push your physical, emotional, or mental limits. The satisfaction of overcoming them can outweigh the temporary discomfort they bring.
The Paradox of Pain and Pleasure
Philosophers like Diogenes and Nietzsche understood that embracing pain can be a path to greater pleasure. Diogenes, known for his austere lifestyle, believed that intentionally seeking discomfort made him more content than the richest kings of his time. This ancient wisdom reminds us that a life worth living isn’t about avoiding pain but about facing it head-on to build strength, joy, and fulfillment.
So, instead of viewing discomfort as the enemy, let’s see it as an ally. By stepping outside our comfort zones, we can rediscover what it means to truly thrive. As Nietzsche said, what we need is “a bit of Cynicism, a little bit of the tub”—a call to embrace just enough difficulty to make our lives richer, fuller, and more rewarding.
Reclaiming Resilience:
What’s one way you can intentionally add a little discomfort to your life this week? Whether it’s skipping the elevator, spending 10 minutes in the cold, or saying no to dessert, let these small changes lead you toward greater resilience and happiness.
If you’d like to dive a little deeper into this concept:
ACUPUNCTURE | ROCHESTER, NY
Exploring Qi, Part 8: Zang-Fu Qi
In Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Zang-Fu Qi, or Organ Qi, represents the specific energy of each organ and its role in maintaining balance and health in the body. Every organ in the body has its own Qi, which governs its unique functions, and these energies work together in harmony to sustain life. When the Qi of an organ is strong, it performs its role efficiently, contributing to overall vitality.
Zang-Fu Qi: The Energy of Organ Harmony
In Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Zang-Fu Qi, or Organ Qi, represents the specific energy of each organ and its role in maintaining balance and health in the body. Every organ in the body has its own Qi, which governs its unique functions, and these energies work together in harmony to sustain life. When the Qi of an organ is strong, it performs its role efficiently, contributing to overall vitality. When it becomes weak or stagnant, imbalances arise, affecting not just the organ itself but the entire system.
In this post, we’ll explore the concept of Organ Qi, its role in health, and how to support the flow of energy through the organs for optimal well-being.
What is Zang-Fu Qi?
Zang-Fu Qi refers to the Qi associated with the Zang (Yin organs) and Fu (Yang organs) in the body. Each organ has a distinct function and corresponding Qi that drives its activities. Together, the Zang-Fu organs form a complex, interdependent system that regulates every aspect of physical, mental, and emotional health.
Here’s a brief overview of the Zang and Fu organs:
• Zang (Yin Organs): Heart, Lungs, Spleen, Liver, and Kidneys. These organs are primarily responsible for storing vital substances like blood, Qi, and essence, and they play key roles in maintaining balance within the body.
• Fu (Yang Organs): Stomach, Small Intestine, Large Intestine, Gallbladder, and Urinary Bladder. These organs are more active and dynamic, focusing on digestion, transformation, and elimination.
The Qi of each organ governs its specific functions, but the organs also work in partnership. For example, the Lungs and Large Intestine have a close energetic relationship, as do the Heart and Small Intestine. Understanding these relationships is key to achieving and maintaining balance.
The Role of Zang-Fu Qi in the Body
Zang-Fu Qi ensures that each organ can perform its unique function while maintaining harmony with the rest of the body. Here’s how the Qi of the major organs contributes to overall health:
1. Heart Qi
• Governs blood circulation and the mind (Shen).
• Supports emotional balance and mental clarity.
• A healthy Heart Qi manifests as a calm mind, steady pulse, and emotional resilience.
2. Lung Qi
• Regulates respiration and the intake of Qi from the air.
• Supports Wei Qi (Defensive Qi) and immunity.
• Healthy Lung Qi shows as deep, smooth breathing and strong resistance to illness.
3. Spleen Qi
• Oversees digestion and the transformation of food into Gu Qi (Food Qi).
• Manages blood production and prevents bleeding.
• Balanced Spleen Qi manifests as strong digestion, mental focus, and energy.
4. Liver Qi
• Regulates the smooth flow of Qi throughout the body.
• Stores blood and supports emotional balance.
• Healthy Liver Qi is seen in smooth digestion, steady emotions, and clear vision.
5. Kidney Qi
• Stores Jing (Essence) and governs growth, reproduction, and aging.
• Regulates water metabolism and supports the bones and marrow.
• Strong Kidney Qi shows as robust vitality, strong bones, and fertility.
6. Stomach Qi
• Breaks down food and prepares it for transformation into Gu Qi.
• Healthy Stomach Qi manifests as good appetite and smooth digestion.
7. Small Intestine Qi
• Separates pure substances from impure, aiding in digestion and absorption.
• Balanced Small Intestine Qi supports nutrient absorption and waste elimination.
8. Large Intestine Qi
• Governs the final stage of digestion and elimination of waste.
• Healthy Large Intestine Qi shows in regular, smooth bowel movements.
9. Gallbladder Qi
• Stores and excretes bile, aiding in digestion.
• Healthy Gallbladder Qi contributes to decisiveness and good digestion.
10. Urinary Bladder Qi
• Stores and excretes urine, regulating water balance.
• Balanced Bladder Qi ensures smooth urination and fluid metabolism.
Signs of Strong and Weak Organ Qi
When Zang-Fu Qi is balanced, you experience:
• Smooth digestion and elimination
• Steady energy levels
• Emotional balance and mental clarity
• Strong immunity and resistance to illness
• A sense of overall vitality and harmony
When Organ Qi becomes imbalanced, you may notice:
• Digestive issues like bloating, constipation, or diarrhea
• Fatigue or lack of energy
• Emotional instability, such as anxiety or irritability
• Respiratory problems like shortness of breath
• Reproductive or hormonal imbalances
How to Support Zang-Fu Qi
Strengthening and harmonizing Organ Qi is essential for maintaining health and preventing illness. Here are some ways to support Zang-Fu Qi:
1. Eat According to the Seasons
Eating seasonal foods that are aligned with nature’s rhythms supports the organs’ unique needs. For example, warming foods like soups and root vegetables are beneficial in winter to support Kidney Qi, while lighter, cooling foods like fruits and greens nourish Liver Qi in the spring.
2. Acupuncture for Balance
Acupuncture is highly effective in restoring balance to Organ Qi. By stimulating specific points related to the Zang-Fu organs, acupuncture helps regulate energy flow, address imbalances, and support overall harmony.
3. Mindful Eating
Paying attention to what and how you eat supports the Spleen and Stomach, the organs responsible for transforming food into Qi. Avoid overeating, eating late at night, or consuming excessive cold or raw foods, as these can weaken Organ Qi.
4. Herbal Medicine
Chinese herbal formulas are tailored to support specific organs and their functions. For example, herbs that nourish Kidney Qi may be used to address fatigue and reproductive issues, while Liver Qi formulas can help alleviate stress and tension.
5. Practice Qi Gong or Tai Chi
These practices promote the smooth flow of Qi through the organs, improving circulation, digestion, and emotional balance. They are particularly effective in relieving stagnation of Liver Qi and supporting overall harmony.
6. Emotional Well-Being
Each organ is associated with specific emotions, and imbalances in these emotions can affect Organ Qi. For example, excessive worry can weaken Spleen Qi, while unprocessed anger can disrupt Liver Qi. Practices like meditation, journaling, and counseling can help you process and balance your emotions, supporting healthy Organ Qi.
The Harmony of Zang-Fu Qi
Zang-Fu Qi is the foundation of health, with each organ contributing its unique energy to maintain balance and harmony in the body. By supporting the Qi of each organ through mindful living, nourishing foods, and practices like acupuncture and Qi Gong, you can strengthen your Zang-Fu Qi and enjoy vibrant health and well-being.
In this series, we’ve explored the many forms of Qi in Classical Chinese Medicine, each with its unique role in sustaining life. Together, they form a holistic system that highlights the interconnectedness of the body, mind, and spirit—a powerful reminder of the harmony that lies at the heart of health.
ACUPUNCTURE | ROCHESTER, NY
Exploring Qi, Part 7: Zheng Qi
In Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Zheng Qi, or Upright Qi, represents the body’s overall strength and vitality. Zheng Qi is the harmonious integration of all the body’s protective and nourishing energies, working together to maintain health and resist disease. It’s a reflection of your body’s ability to stay balanced and resilient in the face of challenges, whether they come from external pathogens or internal imbalances.
Zheng Qi: The Upright Energy That Defends and Sustains
In Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Zheng Qi, or Upright Qi, represents the body’s overall strength and vitality. Zheng Qi is the harmonious integration of all the body’s protective and nourishing energies, working together to maintain health and resist disease. It’s a reflection of your body’s ability to stay balanced and resilient in the face of challenges, whether they come from external pathogens or internal imbalances.
In this post, we’ll explore what Zheng Qi is, how it functions, and how you can cultivate this essential energy to build robust health and resilience.
Zheng Qi: The Upright Energy That Defends and Sustains
In Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Zheng Qi, or Upright Qi, represents the body’s overall strength and vitality. Zheng Qi is the harmonious integration of all the body’s protective and nourishing energies, working together to maintain health and resist disease. It’s a reflection of your body’s ability to stay balanced and resilient in the face of challenges, whether they come from external pathogens or internal imbalances.
In this post, we’ll explore what Zheng Qi is, how it functions, and how you can cultivate this essential energy to build robust health and resilience.
The Role of Zheng Qi in the Body
Zheng Qi serves as the body’s unifying energy, supporting physical, mental, and emotional health. Its key functions include:
1. Defending Against Disease
Zheng Qi is the body’s primary defense against both external pathogens (such as viruses and bacteria) and internal imbalances (like emotional stress or organ dysfunction). It ensures that the body’s immune system remains strong and responsive, preventing illness and aiding in recovery when challenges arise.
2. Maintaining Balance and Harmony
Zheng Qi works to maintain balance within the body, ensuring that all forms of Qi flow smoothly and harmoniously. This balance is essential for keeping the body’s systems aligned and functioning efficiently.
3. Promoting Recovery and Healing
Zheng Qi plays a vital role in the body’s ability to heal from illness or injury. It supports regeneration and repair, allowing the body to restore itself after physical or emotional stress.
4. Sustaining Vitality
Zheng Qi is the essence of resilience and vitality. When Zheng Qi is abundant, you feel energetic, vibrant, and capable of handling life’s challenges with ease.
Signs of Strong and Weak Zheng Qi
When Zheng Qi is strong, you will likely experience:
• Rarely getting sick
• Quick recovery from illness or injury
• Stable energy levels and vitality
• Emotional balance and mental clarity
• A robust immune system that adapts well to environmental changes
When Zheng Qi is weak, you may notice:
• Frequent colds, flu, or infections
• Chronic fatigue or lack of stamina
• Slow healing or recovery from illness
• Emotional instability, such as anxiety or irritability
• Susceptibility to stress and environmental changes
How to Strengthen Zheng Qi
Building and maintaining strong Zheng Qi requires a holistic approach that supports all forms of Qi and promotes balance in the body. Here’s how you can cultivate and protect your Zheng Qi:
1. Nourish Your Body with Whole Foods
Zheng Qi relies on the quality of the energy derived from food (Gu Qi). Eating nutrient-dense, whole foods that are easy to digest—such as warm soups, whole grains, vegetables, and lean proteins—provides the foundation for strong Zheng Qi. Avoid processed, cold, or heavy foods that can weaken digestion and disrupt energy flow.
2. Support Your Immune System
Practices that strengthen Wei Qi (Defensive Qi), such as moderate exercise, acupuncture, and herbal medicine, can help protect your body from external pathogens. Ensuring your lungs and spleen are healthy is particularly important for maintaining strong Zheng Qi.
3. Rest and Rejuvenate
Adequate sleep and rest are essential for allowing Zheng Qi to recharge and restore itself. Overwork, lack of sleep, and chronic stress can drain your Zheng Qi, leaving you vulnerable to illness. Establishing a consistent sleep routine and taking time for relaxation can help preserve this vital energy.
4. Practice Qi Gong or Tai Chi
These gentle, flowing exercises are specifically designed to cultivate and harmonize Zheng Qi. Qi Gong and Tai Chi promote the smooth flow of energy throughout the body, enhancing your vitality and strengthening your defenses.
5. Manage Stress Effectively
Emotional stress can disrupt the flow of Qi, weakening your Zheng Qi over time. Practices such as meditation, deep breathing, journaling, or acupuncture can help reduce stress and restore balance, protecting your body’s Upright Qi.
6. Protect Your Energy
Pay attention to your environment and avoid exposure to excessive cold, dampness, or wind, which can weaken Zheng Qi. Dress appropriately for the weather, and use practices like acupuncture or herbal medicine to support your body during seasonal transitions.
The Power of Upright Qi
Zheng Qi is the unifying energy that defends, sustains, and energizes the body. It reflects your overall health, resilience, and ability to recover from life’s challenges. By nourishing your body with wholesome foods, managing stress, and practicing mindful movement, you can strengthen your Zheng Qi and enjoy a life of vitality and balance.
In the following posts in this series, we’ll continue exploring the other forms of Qi in Classical Chinese Medicine, uncovering their unique roles in supporting health and harmony.
ACUPUNCTURE | ROCHESTER, NY
Exploring Qi, Part 6: Jing Qi
In Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Jing Qi, or Essence, is considered the most fundamental and precious energy in the body. Jing Qi is the root of life—it governs growth, development, reproduction, and aging, forming the foundation for all other types of Qi. Unlike other forms of Qi, which can be replenished through food and air, Jing Qi is finite, making it essential to nurture and protect this vital essence throughout life.
Jing Qi: The Essence of Life and Longevity
In Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Jing Qi, or Essence, is considered the most fundamental and precious energy in the body. Jing Qi is the root of life—it governs growth, development, reproduction, and aging, forming the foundation for all other types of Qi. Unlike other forms of Qi, which can be replenished through food and air, Jing Qi is finite, making it essential to nurture and protect this vital essence throughout life.
In this post, we’ll explore what Jing Qi is, how it functions, and how to preserve this life-sustaining energy for long-term health and vitality.
What is Jing Qi?
Jing Qi, often referred to as Essence, is a unique and essential form of energy stored in the Kidneys. It is the foundational energy that supports all aspects of physical, mental, and spiritual health. Jing Qi can be understood in two forms:
1. Prenatal Jing: This is the energy we inherit from our parents at conception. It determines our constitutional strength, vitality, and genetic potential. Prenatal Jing is finite and cannot be replenished, making it crucial to protect and conserve.
2. Postnatal Jing: This is the energy we acquire from the nourishment of food, drink, and air, processed by the Spleen, Stomach, and Lungs. While Postnatal Jing supports and supplements the body’s overall energy, it is not a substitute for the finite Prenatal Jing.
Together, these two forms of Jing Qi determine the quality and quantity of our life force, influencing everything from growth and development to the aging process.
The Role of Jing Qi in the Body
Jing Qi governs many of the body’s most vital processes and is often likened to the body’s “master resource.” Its functions include:
1. Growth and Development
Jing Qi is the driving force behind physical growth and development. It governs the formation of bones, muscles, and organs, as well as puberty, fertility, and reproductive health. Jing Qi ensures proper maturation and provides the energy for the body to reach its full potential.
2. Reproduction and Fertility
Jing Qi plays a critical role in reproductive health. It provides the energy needed for conception, pregnancy, and childbirth. In men, Jing Qi supports sperm production and reproductive vitality, while in women, it governs ovulation and the health of the menstrual cycle.
3. Aging and Longevity
The state of your Jing Qi influences how you age. As Jing Qi depletes over time, signs of aging begin to appear, such as gray hair, weakened bones, and decreased vitality. Protecting Jing Qi is key to maintaining health and delaying the effects of aging.
4. Healing and Regeneration
Jing Qi supports the body’s ability to heal and regenerate tissues. It provides the energy needed for recovery from illness or injury, ensuring that the body can repair itself efficiently.
5. Immune Strength
Jing Qi is closely linked to the body’s overall strength and resistance to disease. While it is not the same as Wei Qi (Defensive Qi), Jing Qi provides the foundational energy that supports the immune system and the body’s ability to recover from illness.
Signs of Strong and Weak Jing Qi
When Jing Qi is abundant, you may notice:
• Strong bones, teeth, and hair
• Good fertility and reproductive health
• A youthful appearance and steady energy
• Quick recovery from illness or injury
• Robust physical and mental resilience
When Jing Qi is weak or depleted, you may experience:
• Premature aging, such as gray hair or wrinkles
• Weak bones, joint pain, or dental issues
• Infertility or hormonal imbalances
• Fatigue and a lack of stamina
• Poor memory or cognitive decline
How to Preserve and Protect Jing Qi
Since Jing Qi is finite and difficult to replenish, protecting and conserving it is essential for long-term health and vitality. Here are some ways to nurture your Jing Qi:
1. Get Adequate Rest
Rest and sleep are critical for preserving Jing Qi. Overwork, lack of sleep, and chronic stress deplete Jing Qi, leaving the body vulnerable to fatigue and illness. Aim for consistent, high-quality sleep to allow your body to regenerate and restore its essence.
2. Eat Nourishing Foods
A diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods helps support Postnatal Jing and overall energy. Foods that nourish the Kidneys—such as black sesame seeds, walnuts, kidney beans, and dark leafy greens—are particularly beneficial. Avoid excessive alcohol, caffeine, and processed foods, which can weaken the Kidneys and deplete Jing Qi.
3. Practice Gentle Movement
Practices like Qi Gong, Tai Chi, and Yoga help conserve Jing Qi by harmonizing the body’s energy without overexertion. These gentle forms of movement promote balance and circulation, protecting the body from strain and depletion.
4. Moderate Sexual Activity
In CCM, excessive sexual activity is believed to deplete Jing Qi, particularly in men. Moderation and mindful connection in intimacy can help protect Jing Qi while still nurturing relationships and emotional well-being.
5. Reduce Stress
Chronic stress can place a heavy burden on the Kidneys and deplete Jing Qi over time. Practices like meditation, deep breathing, and acupuncture can help calm the mind, protect the Kidneys, and conserve your body’s essence.
6. Support Your Kidneys with Acupuncture
Acupuncture treatments that focus on the Kidney meridian can help strengthen and protect Jing Qi, improving overall vitality and resilience. Regular acupuncture can also help balance emotions and reduce stress, both of which support the preservation of Jing Qi.
7. Connect with Nature
Spending time in nature can have a grounding and restorative effect, helping to nurture Jing Qi. Whether it’s walking in the woods or simply enjoying fresh air, connecting with the natural world supports a deeper sense of balance and vitality.
Conclusion: Honoring the Essence of Life
Jing Qi is the foundation of life—the essence that drives growth, supports fertility, and sustains vitality. While it is finite, you have the power to protect and nurture this vital energy through mindful living, nourishing foods, and practices that support balance and well-being. By honoring your Jing Qi, you can enjoy greater health, resilience, and longevity throughout life.
In future posts, we’ll continue exploring the other types of Qi in Classical Chinese Medicine, revealing how they work together to keep the body in balance and harmony.
ACUPUNCTURE | ROCHESTER, NY
Exploring Qi, Part 5: Wei Qi
In Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Wei Qi, also known as Defensive Qi, acts as the body’s protective shield, defending against external pathogens like cold, wind, and heat. It’s responsible for maintaining the body’s immunity, regulating body temperature, and keeping us safe from illness. While other forms of Qi focus on nourishment and internal support, Wei Qi is all about protection—keeping harmful influences at bay.
Wei Qi: Your Body’s First Line of Defense
In Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Wei Qi, also known as Defensive Qi, acts as the body’s protective shield, defending against external pathogens like cold, wind, and heat. It’s responsible for maintaining the body’s immunity, regulating body temperature, and keeping us safe from illness. While other forms of Qi focus on nourishment and internal support, Wei Qi is all about protection—keeping harmful influences at bay.
In this post, we’ll explore the role of Wei Qi, how it functions, and how you can strengthen this vital energy to stay healthy and resilient in the face of external threats.
What is Wei Qi?
Wei Qi is the Defensive Qi that circulates just beneath the surface of the skin and in the muscles, forming a protective layer that shields the body from external pathogens like cold, wind, dampness, and heat. It is more Yang in nature compared to other forms of Qi, meaning it is fast-moving and active, ready to react to any threats that may arise.
Unlike Ying Qi, which flows through the meridians and blood vessels to nourish the internal organs, Wei Qi is more concerned with protecting the exterior of the body. It patrols the surface of the skin, acting as a sentry that guards the body from external influences. When Wei Qi is strong, we are resistant to illnesses like colds and flu. But when Wei Qi is weak or imbalanced, the body becomes more vulnerable to external pathogens.
The Functions of Wei Qi
Wei Qi serves several essential functions in protecting the body:
1. Defending Against External Pathogens
Wei Qi is the body’s first line of defense against external invaders like viruses, bacteria, and environmental pathogens. It acts like an immune system in CCM, preventing harmful influences from penetrating the body’s exterior. If Wei Qi is strong, the body is more resistant to infections and diseases. If it is weak, the body is more prone to catching colds, flu, or other illnesses.
2. Regulating Body Temperature
Wei Qi helps maintain and regulate body temperature, ensuring that the body remains warm and protected from the cold. It circulates along the skin and muscles, adjusting body heat to match environmental conditions. When Wei Qi is deficient, the body may struggle to stay warm, and you might experience cold hands and feet or an overall sense of chilliness.
3. Protecting the Skin and Muscles
In addition to defending against pathogens, Wei Qi plays a role in maintaining the health of the skin and muscles. It keeps the pores of the skin closed, protecting against wind and dampness. When Wei Qi is balanced, the skin remains healthy, and muscle tissues are strong and resilient.
4. Circulating Between Day and Night
Wei Qi is also dynamic in nature, alternating its activity between day and night. During the day, it circulates on the body’s surface, actively defending against external threats. At night, Wei Qi moves inward to rest and support the organs, particularly the Liver, to prepare the body for the next day’s defense.
Signs of Strong and Weak Wei Qi
When Wei Qi is strong, you will likely experience:
• A strong immune system, rarely getting sick
• Warm, well-regulated body temperature
• Healthy, resilient skin
• Good energy levels throughout the day
• The ability to recover quickly from illness
When Wei Qi is weak, you may notice:
• Frequent colds, flu, or respiratory infections
• Sensitivity to cold weather or drafts
• Cold hands and feet
• Excessive sweating, particularly during the day
• Poor recovery from illness or injury
• Weak, dry, or sensitive skin
How to Strengthen Wei Qi
Strengthening Wei Qi is crucial for maintaining a strong immune system and protecting the body from external pathogens. Here are several ways to build and support this important form of Qi:
1. Eat Foods that Strengthen the Lungs and Spleen
Wei Qi is closely connected to the health of the lungs and spleen, as these organs play a role in its production and circulation. Foods that support lung and spleen health—like warm soups, whole grains, ginger, garlic, and leafy greens—can help build strong Wei Qi. Avoid cold, raw foods, which can weaken the spleen and reduce the strength of your Wei Qi.
2. Practice Qi Gong or Tai Chi
These gentle exercises are excellent for strengthening Wei Qi by improving circulation and promoting balance between the internal and external layers of the body. Qi Gong and Tai Chi help harmonize energy flow and strengthen the body’s natural defenses, making Wei Qi more robust.
3. Acupuncture for Immunity
Acupuncture is a highly effective way to boost Wei Qi, particularly during times when the immune system may be compromised. Acupuncture points that focus on the lungs and the Defensive Layer of the body can help strengthen the body’s natural defenses, improving the flow of Wei Qi and boosting overall immunity.
4. Stay Warm and Avoid Drafts
Since Wei Qi is responsible for maintaining body temperature and defending against cold, it’s important to keep your body warm. Dressing appropriately for the weather, wearing scarves or hats in cold or windy conditions, and avoiding sitting in drafts or damp environments can help protect your Wei Qi from being compromised by external factors.
5. Regular Movement and Exercise
Moderate exercise that promotes circulation is essential for keeping Wei Qi flowing smoothly. Activities like walking, swimming, or gentle jogging help ensure that Wei Qi stays active and responsive, ready to defend the body against threats. However, avoid excessive or strenuous exercise, as this can deplete Qi and weaken the immune system.
6. Manage Stress and Get Adequate Sleep
Stress and lack of sleep can weaken the immune system and make the body more vulnerable to illness. Practicing stress-relieving activities, such as meditation or mindful breathing, can help keep your Wei Qi strong. Additionally, ensuring you get enough restful sleep allows Wei Qi to retreat inward at night to restore itself for the next day.
Wei Qi and Emotional Health
In CCM, the lungs are closely linked to grief and sadness, emotions that can weaken both the lungs and Wei Qi. Prolonged grief or emotional distress can impact the strength of Wei Qi, making you more vulnerable to illness. Managing emotions and finding healthy ways to process grief and sadness can help keep your lungs healthy and protect your Wei Qi.
Guarding Your Body’s Defense System
Wei Qi is the body’s protective force, responsible for defending against illness, regulating body temperature, and maintaining skin and muscle health. By supporting your lungs and spleen, practicing mindful movement, and protecting yourself from external elements, you can strengthen your Wei Qi and boost your overall immunity.
In future posts, we’ll continue exploring other types of Qi in Classical Chinese Medicine, each playing a unique role in maintaining balance and protecting your health.
ACUPUNCTURE | ROCHESTER, NY
Exploring Qi, Part 4: Ying Qi
Ying Qi is the nourishing energy that flows with the blood through the body, providing the necessary sustenance for our organs, tissues, and cells. It is more refined than Gu Qi (Food Qi), as it has undergone further transformation within the body. While Gu Qi is the raw energy extracted from food, Ying Qi is the product of this energy after it has been processed by the spleen, stomach, and lungs.
Ying Qi is the nourishing energy that flows with the blood through the body, providing the necessary sustenance for our organs, tissues, and cells. It is more refined than Gu Qi (Food Qi), as it has undergone further transformation within the body. While Gu Qi is the raw energy extracted from food, Ying Qi is the product of this energy after it has been processed by the spleen, stomach, and lungs.
Ying Qi is sometimes referred to as Nutritive Qi because of its role in nourishing the body at a deep level. It is closely related to the blood in CCM, often described as traveling with the blood through the meridians to ensure the organs are properly nourished and supported. As such, Ying Qi is deeply involved in the processes of healing, regeneration, and overall vitality.
The Role of Ying Qi in the Body
Ying Qi performs several essential functions in the body, including:
1. Nourishing the Organs and Tissues
Ying Qi flows through the meridians, delivering nourishment to every part of the body. It sustains the organs, muscles, skin, and bones, keeping them healthy and functional. Without sufficient Ying Qi, the body’s tissues would become weak, leading to poor health and susceptibility to illness.
2. Supporting Blood Flow
Ying Qi is closely linked with the blood, and the two often flow together through the vessels and meridians. This relationship is essential for ensuring that the body’s tissues receive a steady supply of nutrients and oxygen. When Ying Qi is strong, the blood flows smoothly, supporting good circulation, healing, and overall vitality.
3. Regulating Body Temperature
As Ying Qi circulates through the body, it helps to regulate body temperature, ensuring that the body stays warm and balanced. When Ying Qi is deficient, you might feel cold or experience irregular body temperatures.
4. Aiding in Healing and Regeneration
Ying Qi plays a critical role in the body’s ability to heal from injuries and regenerate damaged tissues. It provides the energy and nutrients needed to repair tissues, support the immune system, and restore balance after illness.
5. Sustaining Emotional and Mental Health
Ying Qi also supports mental clarity, emotional stability, and overall well-being. When Ying Qi is strong, the mind is clear and focused, and emotions remain balanced. Deficient Ying Qi can lead to mental fog, fatigue, and emotional instability.
Signs of Strong and Weak Ying Qi
When Ying Qi is abundant, you will likely experience:
• Strong digestion and appetite
• Good circulation and warm extremities
• Smooth, radiant skin and a healthy complexion
• Mental clarity and emotional stability
• Resilience in healing from illness or injury
When Ying Qi is weak or deficient, you might notice:
• Poor digestion and weak appetite
• Cold hands and feet due to poor circulation
• Fatigue or lack of energy
• Dull or pale skin
• Emotional instability, anxiety, or depression
• Difficulty recovering from illness or wounds
Strengthening and Nourishing Ying Qi
Maintaining strong Ying Qi is key to keeping the body nourished and healthy. Here are several ways to support and strengthen this essential form of energy:
1. Eat Nutrient-Dense Foods
Since Ying Qi is derived from Gu Qi, which comes from food, eating a nutritious, balanced diet is crucial. Foods that are easy to digest and nourishing—such as soups, stews, whole grains, and well-cooked vegetables—support the transformation of Gu Qi into Ying Qi. Avoiding excessive raw or cold foods helps the spleen and stomach process nutrients more effectively.
2. Regulate Your Eating Habits
Eating at regular times, without rushing, helps support your digestive system’s ability to extract the maximum amount of Qi from your food. Avoid overeating or eating too late at night, as these habits can strain the spleen and reduce the production of high-quality Ying Qi.
3. Support Your Blood Health
Since Ying Qi and the blood are closely connected, nourishing the blood also helps to strengthen Ying Qi. Eating iron-rich foods, such as leafy greens, beans, and lean proteins, can support blood production. Acupuncture and certain Chinese herbal formulas can also help promote healthy blood circulation and Qi flow.
4. Practice Qi Gong or Tai Chi
These gentle, flowing exercises are excellent for cultivating and circulating Ying Qi throughout the body. Qi Gong and Tai Chi work by harmonizing the body’s energy, helping you to retain and nourish your Qi while promoting calm and relaxation.
5. Acupuncture for Balance
Regular acupuncture treatments can help balance the flow of Ying Qi in the body, ensuring that the organs are properly nourished. Acupuncture points that focus on the spleen, stomach, and lungs are often used to enhance the body’s ability to produce and circulate Ying Qi effectively.
6. Rest and Sleep
Adequate rest and sleep are critical for nourishing Ying Qi. When the body is at rest, it can focus on healing and regeneration, restoring depleted Qi and strengthening the organs. Aim for a consistent sleep routine and avoid overworking, as excessive stress and fatigue can weaken your Ying Qi over time.
Emotional Health and Ying Qi
In CCM, the spleen is the primary organ responsible for the production of Gu Qi, and it is closely associated with the emotion of worry or overthinking. Excessive worry or mental overwork can weaken the spleen, leading to a deficiency in Ying Qi. Managing stress and emotional health is therefore essential for maintaining strong Ying Qi.
Practices like meditation, journaling, and mindful breathing can help calm the mind and reduce worry, preventing the depletion of vital Qi. Cultivating emotional resilience and learning to manage stress effectively can also help protect your Ying Qi and support long-term health.
Nurturing Your Nutritive Force
Ying Qi is the vital energy that nourishes your body from the inside out. It provides the fuel for healing, regeneration, and daily function, circulating through your meridians and blood vessels to sustain every organ and tissue. By supporting your digestion, managing stress, and nourishing your body with good food and restful sleep, you can maintain strong Ying Qi and enjoy vibrant health.
In future posts, we’ll continue our exploration of the different types of Qi, each playing its own unique role in maintaining balance and vitality in Classical Chinese Medicine.
ACUPUNCTURE | ROCHESTER, NY
Exploring Qi, Part 3: Zong Qi
In Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Zong Qi, also known as Gathering Qi or Ancestral Qi, is one of the most vital forms of energy that powers our daily functions. It serves as a bridge between the food we eat (Gu Qi) and the air we breathe, combining these two fundamental sources of energy to fuel key bodily processes like respiration and circulation.
Zong Qi: The Energy of Breath and Vitality
In Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Zong Qi, also known as Gathering Qi or Ancestral Qi, is one of the most vital forms of energy that powers our daily functions. It serves as a bridge between the food we eat (Gu Qi) and the air we breathe, combining these two fundamental sources of energy to fuel key bodily processes like respiration and circulation.
In this post, we’ll explore what Zong Qi is, how it’s formed, and how you can support its function for optimal health and vitality.
What is Zong Qi?
Zong Qi is created when Gu Qi (the energy extracted from food by the spleen and stomach) rises to the lungs, where it combines with the air we breathe. The lungs play a crucial role in this process, mixing the energy from food with fresh oxygen to produce Zong Qi.
Zong Qi gathers in the chest and has a particularly close relationship with two vital organ systems: the lungs and the heart. It supports the lungs in controlling respiration and oxygen exchange, and it assists the heart in circulating blood throughout the body.
Because Zong Qi directly influences both respiration and circulation, it’s essential for maintaining healthy lung function, strong circulation, and robust energy levels. When Zong Qi is abundant and flowing smoothly, you feel energetic, your breath is full and deep, and your heart pumps blood efficiently throughout the body. When Zong Qi is weak or imbalanced, it can lead to fatigue, shallow breathing, and poor circulation.
The Functions of Zong Qi
Zong Qi performs several critical functions in the body, including:
1. Supporting Lung Function and Respiration
Zong Qi governs the process of breathing, ensuring that the lungs can take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide efficiently. It supports the strength and depth of your breath, helping you feel energized and refreshed with each inhale.
2. Aiding Circulation and Heart Function
Zong Qi helps the heart pump blood effectively throughout the body. It ensures that oxygenated blood reaches all the tissues, muscles, and organs, nourishing them with vital nutrients and energy. Zong Qi also influences blood pressure and circulation, keeping the flow of blood strong and steady.
3. Empowering Voice and Speech
Zong Qi plays a key role in powering your voice. It influences the strength, volume, and clarity of speech. If Zong Qi is weak, your voice may become quiet, hoarse, or lacking in vitality.
4. Promoting Overall Vitality
Since Zong Qi is derived from both food and air, it provides the body with a powerful combination of nutrients and oxygen, fueling daily activities and overall vitality. Healthy Zong Qi leads to abundant energy, clear thinking, and the ability to engage fully with life.
Signs of Strong and Weak Zong Qi
When Zong Qi is strong, you may notice:
• Deep, full breaths
• A strong, clear voice
• Warm hands and feet (a sign of good circulation)
• Steady energy throughout the day
• Good stamina and endurance
When Zong Qi is weak or imbalanced, you may experience:
• Shallow or labored breathing
• Fatigue, especially during physical activity
• Poor circulation, cold extremities
• A weak or quiet voice
• Shortness of breath
• Heart palpitations or irregular heart rhythms
How to Strengthen and Balance Zong Qi
Fortunately, there are several ways to support and strengthen your Zong Qi, ensuring that your lungs and heart receive the energy they need to function optimally.
1. Breathe Deeply and Mindfully
Since Zong Qi is directly linked to the air you breathe, practicing mindful, deep breathing is one of the best ways to strengthen this energy. Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing, Qi Gong, and meditation can help you deepen your breath and improve the flow of Zong Qi. Pay attention to breathing fully into your lungs, filling your chest and abdomen with air.
2. Eat Nutrient-Rich Foods
Strong Zong Qi starts with healthy Gu Qi, which comes from the food you eat. Consuming nutrient-rich, whole foods—especially those that are warm and easily digestible—will provide your body with the raw materials it needs to create high-quality Gu Qi. Warm soups, grains, leafy vegetables, and lean proteins can all help support the transformation of Gu Qi into Zong Qi.
3. Get Fresh Air
Since Zong Qi is formed in the lungs, spending time in fresh, clean air is essential for its strength. Spending time outdoors, especially in nature, can help your lungs absorb fresh oxygen and improve the quality of Zong Qi. If possible, avoid pollution and smoke, which can weaken lung function and disrupt the creation of Zong Qi.
4. Exercise Regularly
Moderate exercise, especially cardiovascular activities like walking, jogging, swimming, or biking, helps improve lung capacity and circulation, two key functions of Zong Qi. Exercise gets the blood flowing and the lungs working, encouraging the production of strong Zong Qi. However, avoid excessive or overly intense workouts, as they can deplete your energy reserves and weaken Qi over time.
5. Support Your Lungs with Acupuncture
Acupuncture can be highly effective in strengthening Zong Qi, especially if lung function or circulation is weak. Acupuncture points that support the lungs and heart can help improve respiration, boost energy, and regulate blood flow. Regular treatments can also help balance Qi throughout the body, preventing stagnation or depletion.
6. Avoid Smoking and Pollutants
Since Zong Qi relies on clean air to function optimally, it’s important to avoid smoking and exposure to environmental pollutants whenever possible. Smoking can damage the lungs and reduce the body’s ability to generate Zong Qi, leading to weakened immunity, shallow breathing, and poor energy levels.
Zong Qi and Emotional Health
In CCM, the lungs are closely associated with the emotions of grief and sadness. Prolonged or unresolved emotional issues can impact the lungs, weakening Zong Qi and leading to imbalances in breathing and energy. Addressing emotional health is therefore an important part of maintaining strong Zong Qi.
Practices such as meditation, talk therapy, and acupuncture can help you process and release stored emotions, preventing them from stagnating in the lungs and disrupting the flow of Qi.
Conclusion: Breathing Life Into Your Vital Energy
Zong Qi is the energy of breath, circulation, and vitality. It’s formed through the delicate balance of nourishment from food and the oxygen we take in through the lungs. When Zong Qi is abundant, you experience deep, full breaths, a strong voice, steady energy, and good circulation. By supporting your lungs, eating well, and practicing mindful breathing, you can strengthen your Zong Qi and enjoy the vitality it brings to your life.
In upcoming posts, we’ll continue our journey through the different types of Qi in Classical Chinese Medicine, exploring how each one contributes to your overall health and well-being.
ACUPUNCTURE | ROCHESTER, NY
Exploring Qi, Part 2: Gu Qi
In Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Qi is the fundamental energy that sustains life, flowing through the body and powering every function. One of the most vital forms of this energy is Gu Qi—the energy derived from the food we eat. While many think of food simply as fuel, in CCM, the transformation of food into energy is a sacred process that directly influences our health, vitality, and overall well-being.
Gu Qi: The Nourishing Energy Derived from Food
In Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Qi is the fundamental energy that sustains life, flowing through the body and powering every function. One of the most vital forms of this energy is Gu Qi—the energy derived from the food we eat. While many think of food simply as fuel, in CCM, the transformation of food into energy is a sacred process that directly influences our health, vitality, and overall well-being.
In this post, we’ll dive deep into Gu Qi, its role in the body, and how to optimize your diet and lifestyle to enhance this nourishing energy.
What is Gu Qi?
Gu Qi, also known as Food Qi, is the energy extracted from the food we consume. It is the first stage in the complex process of Qi production and plays a foundational role in creating the various forms of Qi that sustain the body.
The process begins in the spleen and stomach, which are responsible for breaking down food and extracting its essence. The spleen and stomach are referred to as the "Middle Jiao" in CCM, representing the core of the digestive system. Once the food has been processed, it is transformed into a raw form of energy called Gu Qi.
However, Gu Qi is not yet ready to circulate through the body and nourish the organs. It must first combine with the air we breathe (a process handled by the lungs) to form Zong Qi (Gathering Qi), which then helps fuel the body’s various functions.
The Role of Gu Qi in the Body
Gu Qi’s primary role is to provide the raw materials for the creation of more refined forms of Qi, such as Ying Qi (Nutritive Qi) and Wei Qi (Defensive Qi). But before it can be transformed into these other forms, Gu Qi must be of high quality and flow smoothly through the body.
If the body is efficient at transforming food into Gu Qi, you can expect:
Stronger immunity: Healthy Gu Qi leads to better Wei Qi (Defensive Qi), which protects the body from external pathogens.
More vitality: Abundant Gu Qi is a source of energy that drives all the body’s functions, from digestion to circulation.
Better digestion: A well-functioning spleen and stomach will convert food into usable energy more efficiently, reducing symptoms like bloating, indigestion, or fatigue after meals.
However, if Gu Qi is weak or deficient, it can manifest in several health problems, such as:
Fatigue and sluggishness: Without proper energy from food, the body lacks the fuel it needs to stay active and alert.
Poor digestion: Issues like bloating, poor appetite, or indigestion can arise when the spleen and stomach are unable to properly extract Gu Qi from food.
Weakened immunity: Since Gu Qi is the foundation of Defensive Qi (Wei Qi), deficiencies in Gu Qi can leave the body vulnerable to illness.
The Transformation of Gu Qi
The journey of Gu Qi doesn’t stop once food is broken down in the spleen and stomach. After its initial extraction, Gu Qi is sent to the lungs, where it combines with the air we breathe to create Zong Qi (also called Gathering Qi). Zong Qi supports respiration and circulation, helping to distribute oxygen and nutrients throughout the body.
From there, Zong Qi further transforms into Ying Qi (Nutritive Qi), which nourishes the organs and tissues, and Wei Qi (Defensive Qi), which protects the body from external pathogens. In this way, Gu Qi is the critical building block for the body’s overall energy and protection.
How to Strengthen Gu Qi
Maintaining strong and balanced Gu Qi starts with the food you eat and how well your body can extract energy from it. Here are some tips to optimize your diet and lifestyle for better Gu Qi:
Eat a Balanced, Whole-Food Diet Gu Qi is only as good as the food it’s derived from. Eating fresh, whole foods that are nutrient-dense provides the best raw material for producing Gu Qi. Foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins are especially beneficial. Avoid overly processed or cold foods, which can weaken the digestive system and lead to deficient Gu Qi.
Support Your Spleen and Stomach In Classical Chinese Medicine, the spleen and stomach are the central players in the production of Gu Qi. Foods that are warm, easy to digest, and lightly cooked are easier on the digestive system and help strengthen these organs. Steamed vegetables, soups, and cooked grains are particularly nourishing. Avoid raw, cold foods, and excessive dairy, which can create dampness and weaken digestion.
Chew Your Food Thoroughly Digestion starts in the mouth. Taking time to chew your food properly helps your stomach and spleen work more efficiently in the breakdown and extraction of nutrients, leading to stronger Gu Qi. Mindful eating can also help you tune in to your body’s needs and signals of fullness.
Mind Your Eating Habits Eating too quickly, eating on the go, or overeating can stress the digestive system and interfere with the production of Gu Qi. Aim to eat in a calm, relaxed environment, and avoid heavy meals late at night, as they can burden the spleen and stomach.
Reduce Stress Stress weakens the digestive system, making it harder for the body to transform food into energy. Practices like meditation, deep breathing, and regular acupuncture can help support the spleen and stomach by calming the mind and reducing stress.
Acupuncture to Boost Gu Qi Acupuncture can be highly effective for strengthening the spleen and stomach, ensuring that Gu Qi is produced efficiently. Specific acupuncture points are often used to support digestion and energy production, promoting the smooth transformation of food into energy.
Signs of Gu Qi Deficiency
If your Gu Qi is weak or deficient, your body may give you some early warning signs, including:
Frequent fatigue, especially after eating
Bloating, gas, or indigestion
Poor appetite or a feeling of fullness after small meals
Loose stools or irregular bowel movements
Cold hands and feet
Low immunity, frequent colds, or infections
These symptoms can indicate that the spleen and stomach are struggling to extract energy from food, and your body may not be getting the nutrients it needs to thrive.
Nourishing Your Body’s Energy
Gu Qi is the starting point for all energy production in the body. It is the raw material that transforms into the different types of Qi that power and protect us. By nourishing your digestive system and paying attention to what and how you eat, you can strengthen your Gu Qi, leading to better energy, improved immunity, and greater overall well-being.
ACUPUNCTURE | ROCHESTER, NY
Exploring Qi, Part 1: Yuan Qi
In the world of Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Yuan Qi—often referred to as Original Qi or Source Qi—represents the foundation of our vitality. It’s the root of life, inherited from our parents at conception, and governs growth, development, and the body’s ability to heal. Yuan Qi is one of the most fundamental forms of energy in the body, and understanding it is key to unlocking greater health and longevity.
Yuan Qi: The Foundation of Life and Vitality
In the world of Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Yuan Qi—often referred to as Original Qi or Source Qi—represents the foundation of our vitality. It’s the root of life, inherited from our parents at conception, and governs growth, development, and the body’s ability to heal. Yuan Qi is one of the most fundamental forms of energy in the body, and understanding it is key to unlocking greater health and longevity.
In this post, we’ll explore what Yuan Qi is, how it works, and why nurturing it is essential for maintaining health and vitality throughout life.
What is Yuan Qi?
Yuan Qi is the original essence we receive from our parents at the moment of conception. It’s stored in the kidneys and is considered the body’s most fundamental energy. Unlike other forms of Qi that are replenished through food, air, and lifestyle, Yuan Qi is finite—we cannot generate more of it after birth. For this reason, it’s often described as the “battery” of life: it gives us the energy we need to function, but once it’s depleted, it’s gone.
In Classical Chinese Medicine, Yuan Qi is considered the foundation of all physiological activity. It fuels the body’s growth, supports development during childhood, and sustains us into adulthood. As we age, the gradual depletion of Yuan Qi is associated with the natural aging process, including the decline in vitality and physical resilience.
Functions of Yuan Qi
Yuan Qi plays several key roles in maintaining health and vitality:
1. Growth and Development: Yuan Qi is responsible for the body’s growth and maturation, especially during childhood and adolescence. It supports the development of organs, tissues, and bones, laying the foundation for a strong constitution.
2. Reproductive Health: Yuan Qi governs fertility and reproductive health. It provides the essential energy for conception, pregnancy, and childbirth, making it crucial for both men and women seeking to maintain or enhance fertility.
3. Healing and Regeneration: Yuan Qi supports the body’s ability to heal and recover from illness or injury. It provides the energy needed for cellular repair and regeneration, allowing the body to bounce back from physical or emotional stress.
4. Constitutional Strength: Yuan Qi determines the strength of our constitution, or our ability to resist disease and recover from health challenges. People with abundant Yuan Qi tend to have robust health, strong immunity, and resilience, while those with depleted Yuan Qi may experience chronic health issues and fatigue.
5. The Vitality of the Kidneys: Since Yuan Qi is stored in the kidneys, it’s closely linked to the health of this organ system. Strong kidney function is crucial for preserving Yuan Qi, as the kidneys are responsible for maintaining the balance of fluids and essences that support life.
Yuan Qi and Aging
One of the central ideas in Classical Chinese Medicine is that Yuan Qi is finite. As we age, the body gradually consumes this precious energy. This process is natural, but certain lifestyle factors can accelerate the depletion of Yuan Qi. Stress, poor diet, overwork, and excessive physical exertion can all drain this vital energy, leading to premature aging and health decline.
When Yuan Qi becomes depleted, signs of aging may appear, such as:
• Decreased stamina and strength
• Cognitive decline and memory issues
• Poor immune function
• Fertility challenges
• Chronic fatigue or exhaustion
• Weakness in the bones or joints
While we cannot replenish Yuan Qi, we can take steps to preserve it. By living in alignment with the body’s natural rhythms and practicing mindful self-care, we can slow the depletion of Yuan Qi and maintain vitality well into our later years.
How to Preserve and Nurture Yuan Qi
Although Yuan Qi is finite, there are ways to protect and preserve this essential energy. Here are some practices that support the health of Yuan Qi:
1. Rest and Recovery: Adequate rest is one of the best ways to preserve Yuan Qi. Overworking or depriving the body of sleep can lead to rapid depletion, while regular periods of rest and recovery allow the body to recharge and maintain balance.
2. Balanced Diet: Eating a nutrient-rich, balanced diet helps support the body’s overall energy, indirectly protecting Yuan Qi. Warm, nourishing foods that are easy to digest (like soups, stews, and whole grains) are especially beneficial.
3. Mindful Exercise: While physical activity is important for overall health, excessive or strenuous exercise can deplete Yuan Qi. Practices like Qi Gong, Tai Chi, and gentle yoga help cultivate energy without draining the body’s reserves.
4. Stress Management: Chronic stress can accelerate the depletion of Yuan Qi. Practices that reduce stress, such as meditation, deep breathing, and acupuncture, help protect the body’s energy reserves and support long-term health.
5. Acupuncture: Acupuncture treatments can help balance the flow of Qi in the body, supporting the kidneys and other organ systems that are responsible for preserving Yuan Qi. Regular acupuncture can also help alleviate stress and improve overall vitality.
6. Connection to Nature: Spending time in nature, whether through mindful walks or simply sitting outdoors, can help restore a sense of peace and balance, indirectly protecting Yuan Qi. Nature has a calming and restorative effect on both mind and body.
Yuan Qi in Reproductive Health
In CCM, Yuan Qi is closely linked to reproductive health. For both men and women, Yuan Qi governs the ability to conceive, carry a pregnancy, and give birth. Fertility treatments in Classical Chinese Medicine often focus on strengthening Yuan Qi and supporting the kidneys, which are the foundation of reproductive energy.
For women, Yuan Qi is also vital during pregnancy and childbirth, ensuring the health of both mother and child. For men, Yuan Qi supports sperm production and overall reproductive vitality. Protecting Yuan Qi through mindful lifestyle practices is essential for those who want to maintain reproductive health and vitality as they age.
Protecting Your Life’s Essence
Yuan Qi is the essence of life, the original energy that fuels our growth, vitality, and resilience. While it is finite, we have the power to protect and preserve it through mindful practices that support balance and harmony. By living in alignment with nature, nurturing our bodies, and managing stress, we can safeguard our Yuan Qi and enjoy a long, healthy, and vibrant life.
In future posts, we’ll continue exploring the other types of Qi, each with its own unique role in maintaining health and well-being.
ACUPUNCTURE | ROCHESTER, NY
Exploring the Different Types of Qi in Classical Chinese Medicine
In Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Qi is the fundamental energy that flows through every living thing, governing the body’s functions, vitality, and health. While many people may associate Qi simply with energy or life force, the truth is that there are many different types of Qi, each with its own role in maintaining harmony and balance in the body.
In Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM), Qi is the fundamental energy that flows through every living thing, governing the body’s functions, vitality, and health. While many people may associate Qi simply with energy or life force, the truth is that there are many different types of Qi, each with its own role in maintaining harmony and balance in the body.
In this post, we’ll take a broad look at the various forms of Qi that play vital roles in keeping us healthy. In future blogs, we’ll dive deeper into each one, exploring how they influence specific areas of health and well-being.
The Different Types of Qi
Qi can be understood as the dynamic and transformative force that supports all life processes. Classical Chinese Medicine identifies several types of Qi, each with specific functions:
Yuan Qi (Original Qi) Yuan Qi is the foundational energy that is inherited from our parents at conception. It is stored in the kidneys and supports all growth and development. Yuan Qi is often referred to as the source of vitality and is closely linked to the body’s ability to heal and regenerate. Because it’s finite, nurturing Yuan Qi is crucial to maintaining long-term health and longevity.
Gu Qi (Food Qi) Gu Qi is derived from the food and drink we consume. After food is ingested, the spleen and stomach transform it into Gu Qi, which becomes a raw form of energy. Gu Qi doesn’t yet circulate through the body; it first combines with air in the lungs to create Zong Qi (Gathering Qi).
Zong Qi (Gathering Qi) Zong Qi is formed from the combination of Gu Qi and the air we breathe. It gathers in the chest and is responsible for supporting the heart and lungs. Zong Qi plays an essential role in respiration and circulation, providing the body with the energy needed for these vital processes.
Ying Qi (Nutritive Qi) Ying Qi, also known as Nutritive Qi, circulates within the blood vessels and meridians, nourishing the organs and tissues. It’s closely tied to the function of the blood and is responsible for sustaining and maintaining the body. Ying Qi plays a critical role in providing nourishment and is essential for healing and regeneration.
Wei Qi (Defensive Qi) Wei Qi is the protective energy that circulates on the surface of the body. It acts as the first line of defense against external pathogens like wind, cold, and heat. Wei Qi is also responsible for regulating body temperature and ensuring the skin and muscles remain strong and resilient. A strong Wei Qi protects against illness, while a weakened Wei Qi can lead to susceptibility to colds, flus, and other external invasions.
Jing Qi (Essence) Jing Qi is closely related to Yuan Qi but is often discussed in its own right. Jing is the essence of life, stored in the kidneys, and it governs growth, reproduction, and development. Jing Qi is more substantial and slower-moving than other forms of Qi, and it’s considered the core of our vitality and longevity.
Zheng Qi (Upright Qi) Zheng Qi is the body’s overall strength and resistance to disease. It encompasses the harmonious functioning of all the body’s energies, including Yuan Qi, Wei Qi, and Ying Qi. Strong Zheng Qi indicates that the body can effectively resist illness, while weakened Zheng Qi leaves the body vulnerable to disease.
Qi of the Organs (Zang-Fu Qi) Each of the major organs in the body has its own Qi that governs its specific function. For example, Lung Qi is responsible for respiration, Heart Qi governs circulation and emotions, and Kidney Qi supports reproductive health and fluid balance. Organ Qi ensures that each organ performs its role efficiently, contributing to overall balance.
How Qi Works Together
The different types of Qi are not isolated—they work together to keep the body balanced and healthy. For example, Gu Qi derived from food must combine with air to become Zong Qi, which then supports the body’s respiration and circulation. Similarly, Wei Qi and Ying Qi work in harmony to protect and nourish the body, respectively. When these different types of Qi are in balance, the body thrives. When they become deficient or blocked, illness can arise.
Nurturing and Balancing Qi
Maintaining the balance of Qi is key to health in Classical Chinese Medicine. Many factors, such as diet, stress, sleep, and emotional health, influence the strength and balance of our Qi. Practices like acupuncture, Qi Gong, herbal medicine, and mindful breathing can help regulate and strengthen Qi, restoring harmony in the body.
The Journey of Qi Begins
Understanding the different types of Qi helps us appreciate the complexity of energy flow within the body and how it supports every aspect of health. In future blogs, we’ll take a deeper dive into each type of Qi, exploring how they function, what happens when they become imbalanced, and how you can strengthen and support them to achieve better health and well-being.
ACUPUNCTURE | ROCHESTER, NY
Gu Syndrome: Ancient Wisdom for Modern Complex Illness
Gu syndrome is an ancient concept in classical Chinese medicine that addresses chronic, lingering conditions often characterized by mysterious symptoms that don’t respond to conventional treatments. Though largely removed from modern Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) curricula, this syndrome offers valuable insights into treating persistent physical and psychological ailments.
Gu syndrome is an ancient concept in classical Chinese medicine that addresses chronic, lingering conditions often characterized by mysterious symptoms that don’t respond to conventional treatments. Though largely removed from modern Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) curricula, this syndrome offers valuable insights into treating persistent physical and psychological ailments.
What is Gu Syndrome?
In classical Chinese medicine, Gu syndrome was associated with "possession" by pathogenic influences, often referred to metaphorically as "demons" or "dark forces." The original character for Gu depicts three worms in a pot, symbolizing the harmful elements that can invade the body and "hollow out" one's health from the inside. This may involve various pathogens—physical or otherwise—that undermine the body’s vitality, leading to chronic conditions marked by digestive issues, fatigue, neurological symptoms, and even mood disturbances.
Types and Symptoms
Gu syndrome can present in two primary forms: "Brain Gu" and "Digestive Gu," though many cases exhibit overlapping symptoms.
Brain Gu: Symptoms often include nervous system disturbances such as anxiety, depression, chronic fatigue, fibromyalgia, headaches, and even visual or auditory hallucinations. These cases often involve chronic viral infections or other elusive pathogens like Lyme disease.
Digestive Gu: This form is marked by chronic gastrointestinal symptoms such as bloating, gas, irregular bowel movements, and strange sensations in the abdomen. Patients may also experience "brain fog" or mild psychological symptoms like bad dreams.
In both forms, a hallmark of Gu syndrome is the presence of symptoms that defy standard diagnostic categories and persist despite conventional treatment efforts.
A Complex, Integrated Approach
Gu syndrome's treatment diverges from standard TCM practices, emphasizing a multi-layered herbal approach. Unlike conventional methods that categorize symptoms into "hot vs. cold" or "internal vs. external," Gu treatment employs an interwoven strategy, combining herbs with different properties. Each herb is selected for its ability to both combat pathogens and strengthen the body's internal reserves.
Key Herbal Categories in Gu Treatment
Surface-Resolving Herbs: Herbs that "release the surface" while also addressing underlying pathogenic influences. Examples include baizhi (Angelica), zisu (Perilla), and bohe (Mint).
Qi Tonics: Raw gancao (Licorice) and huangqi (Astragalus) serve to bolster qi while possessing anti-pathogenic properties.
Blood Tonics: Herbs like danggui (Angelica sinensis) and chuanxiong (Sichuan lovage) enhance circulation and possess aromatic qualities that act like internal fumigants.
Yin Tonics: To support the nervous system and alleviate "fried nerves," herbs like baihe (Lily bulb), huangjing (Polygonatum), and beishashen (Glehnia) are employed.
Anti-Parasitics: These include qinghao (Artemisia annua) for malaria-like symptoms and shichangpu (Acorus) for both digestive and nervous system disorders.
Aromatic Anti-Parasitics: Strongly aromatic herbs like clove (dingxiang) and garlic target pathogens at different life stages.
Each treatment plan is tailored to the patient, incorporating a variety of herbs to address the underlying imbalances while offering long-term support for the body’s healing.
Long-Term Treatment and Adaptation
Gu syndrome isn’t a condition that resolves quickly. It is often compared to "oil seeping into flour," signifying its pervasive and deeply rooted nature. Even in cases where symptoms improve rapidly, a plateau may follow, requiring continued, adaptable treatment. Regularly changing the herbal prescription every six weeks helps outpace the pathogen's ability to adapt, ensuring steady progress.
For some, the treatment may last six months, while for others dealing with more complex or long-standing conditions, it may extend to three to five years. It is crucial to educate patients about this long-term approach, setting realistic expectations for recovery.
Beyond the Physical: The Mind-Body Connection
The ancient association of Gu with possession and "demons" highlights the intricate mind-body relationship in chronic illness. Many Gu patients experience anxiety, depression, or other psychological symptoms, which may not improve with conventional psychiatric treatments alone. The concept of Gu can provide a framework for understanding how physical pathogens, especially chronic infections or inflammatory conditions, can also impact mental health.
A Modern Revival of an Ancient Practice
Despite its ancient origins, the concept of Gu syndrome may be more relevant than ever. Today’s lifestyles, diets, and medical histories (including extensive antibiotic use) may render modern individuals more susceptible to lingering infections, chronic inflammation, and autoimmune responses. Reviving the understanding of Gu syndrome allows practitioners to explore treatment strategies for conditions that fall outside of conventional medical frameworks.
Integrating Gu Treatment into Contemporary Practice
For practitioners, considering a Gu approach can be transformative when dealing with patients who present with baffling or "incurable" symptoms. It involves recognizing the depth of the syndrome and embracing a treatment plan that goes beyond symptom suppression to restore the body’s harmony from within. The systematic use of herbs that can both heal and defend against pathogens makes it suitable for the long-term treatment required to truly resolve these complex cases.
In cases where the conventional approach doesn’t suffice, viewing the symptoms through the lens of Gu syndrome may offer a path forward. It allows for a broader understanding of how persistent pathogens can manifest as complex, multisystem illnesses, requiring a comprehensive and adaptive approach for healing.
If you’d like to go deeper on Gu Syndrome, please check out this podcast with Dr. Heiner Fruehauf, PhD, LAc. He is the leading expert on the topic among modern day practitioners.
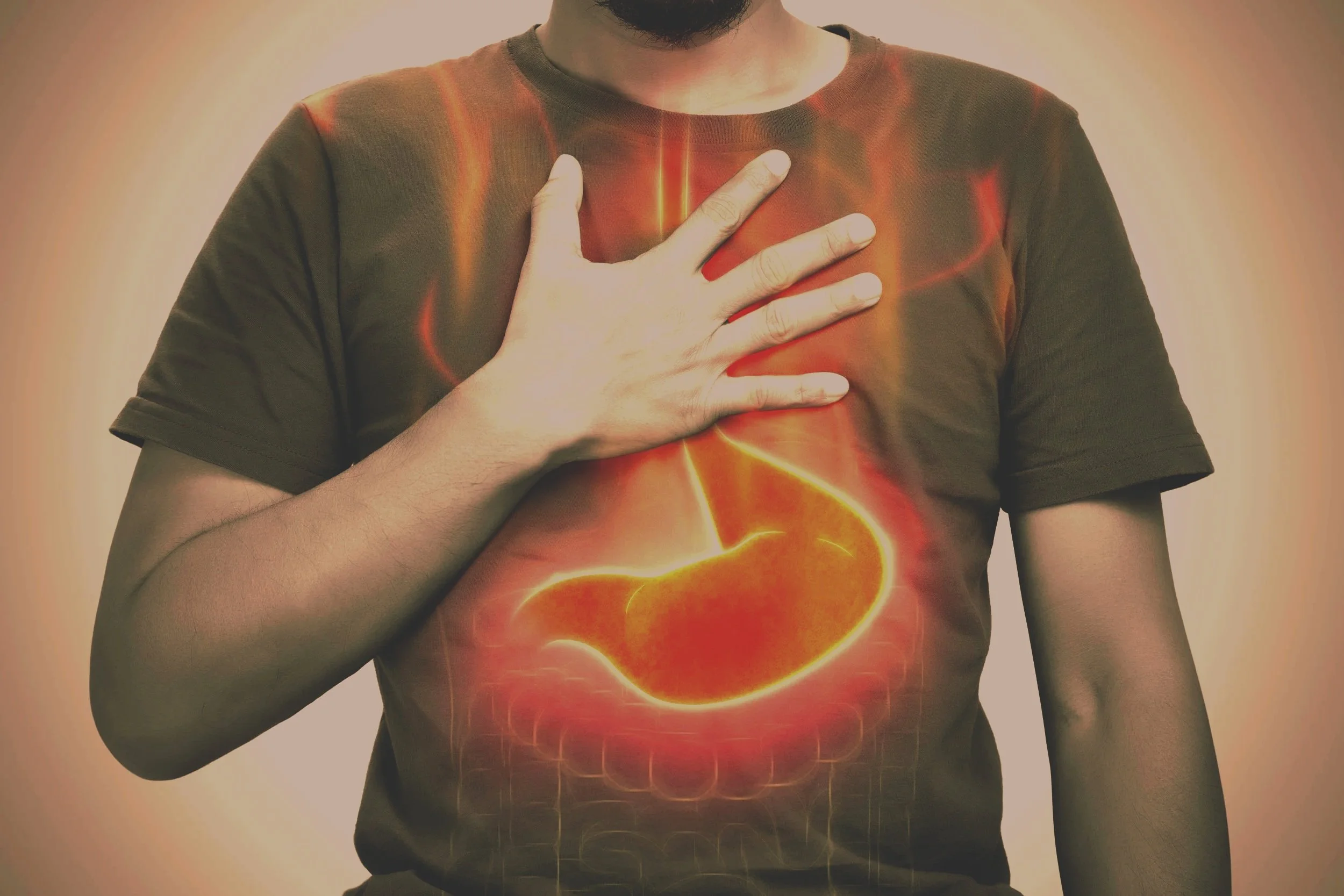































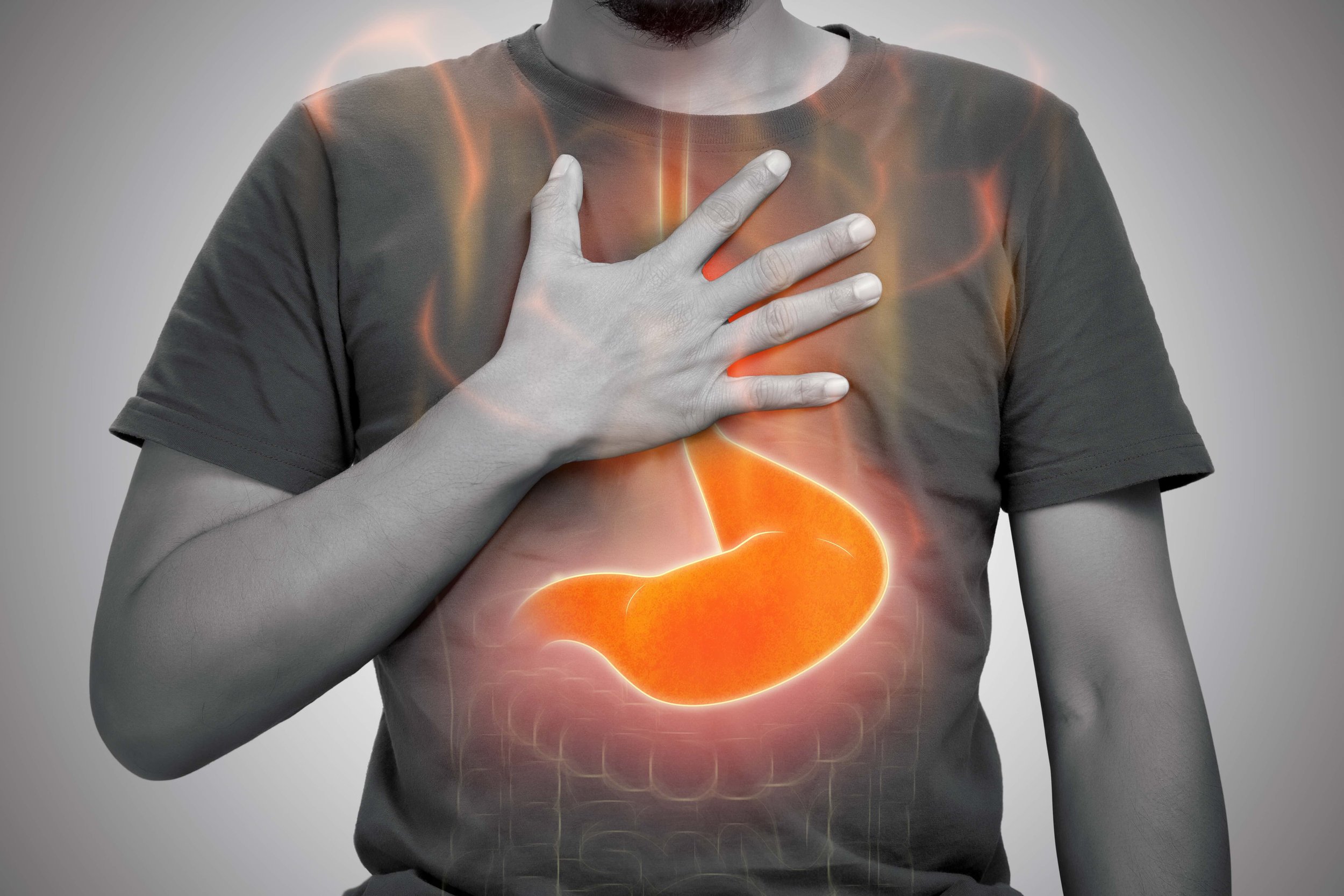








Acid reflux. GERD. Heartburn. Whatever name it goes by, it’s become a staple in the lives of far too many. Whether triggered by stress, food, or an overtaxed system, the burning in the chest and sour taste in the mouth are often treated with quick fixes like antacids or proton pump inhibitors.